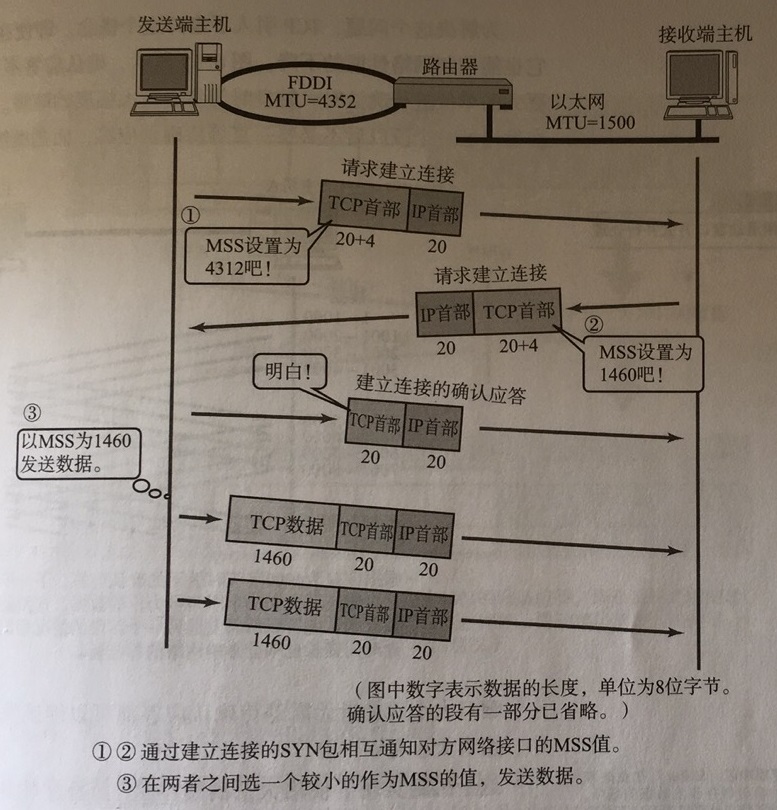
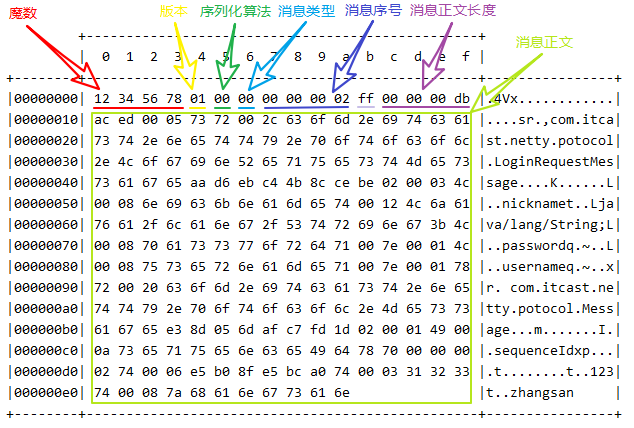
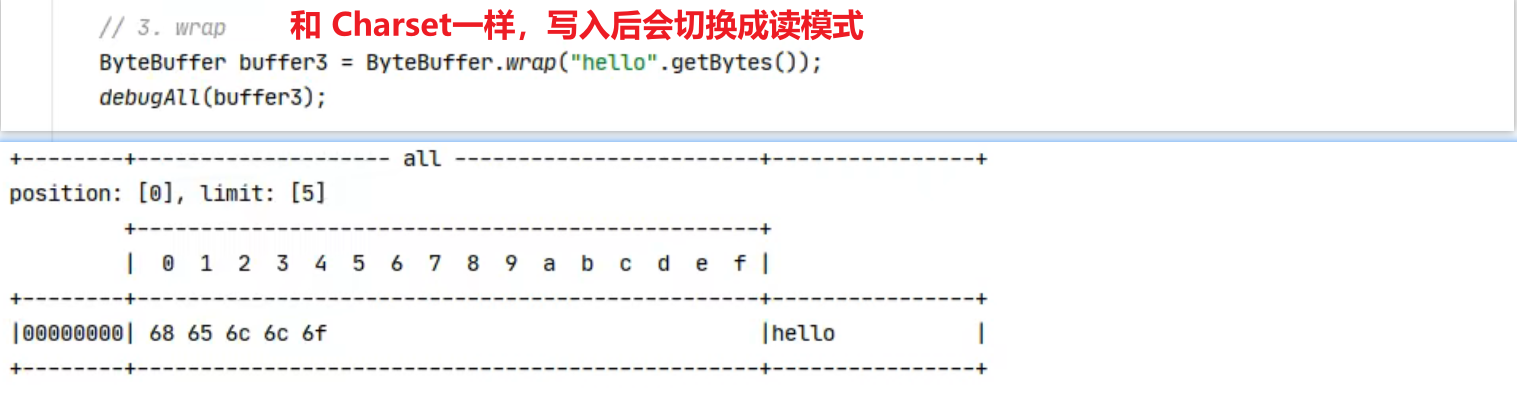
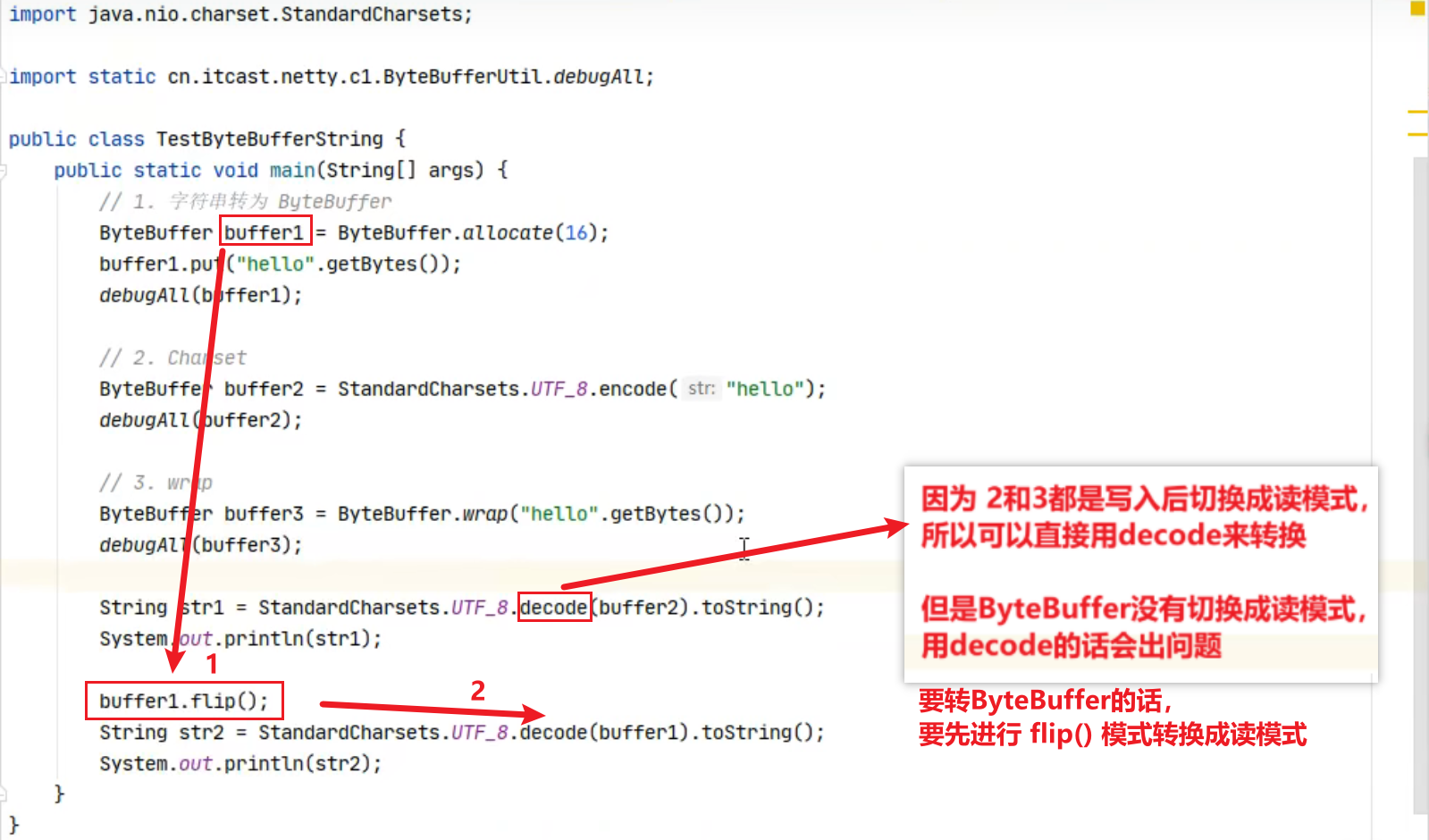
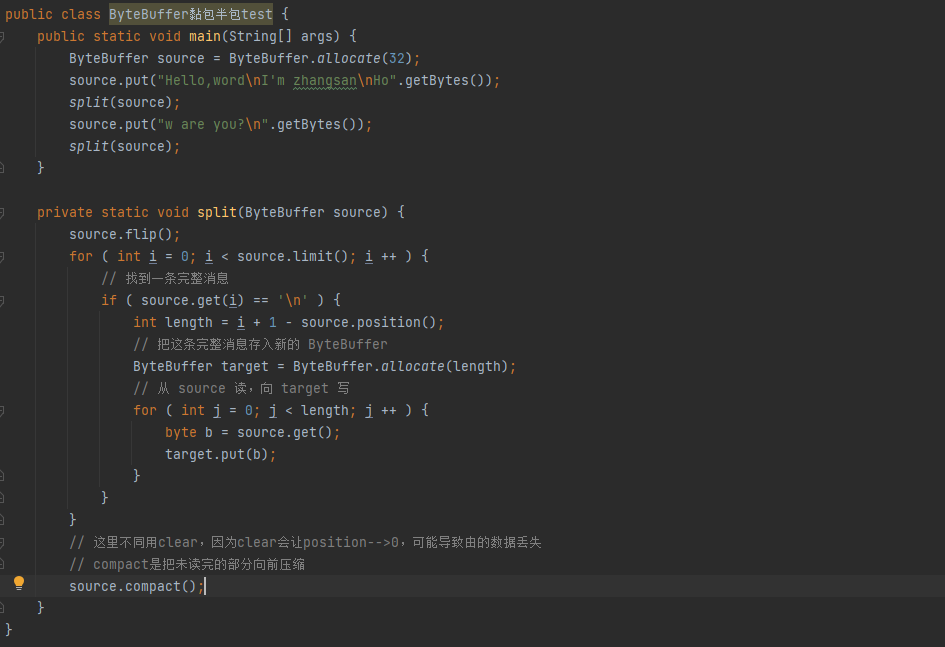
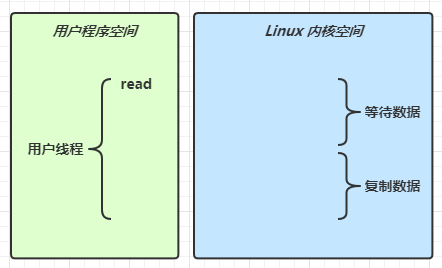
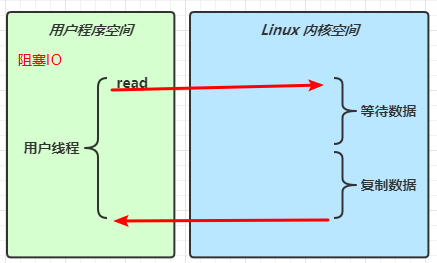
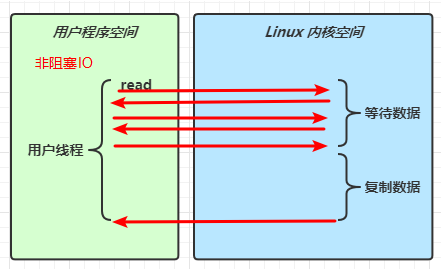
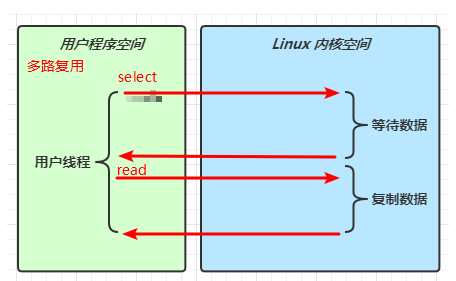
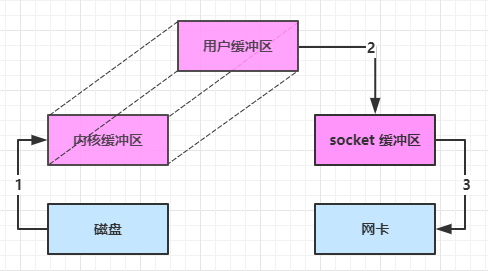
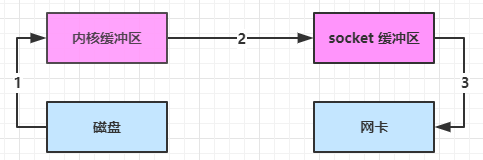
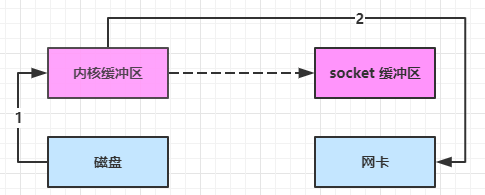
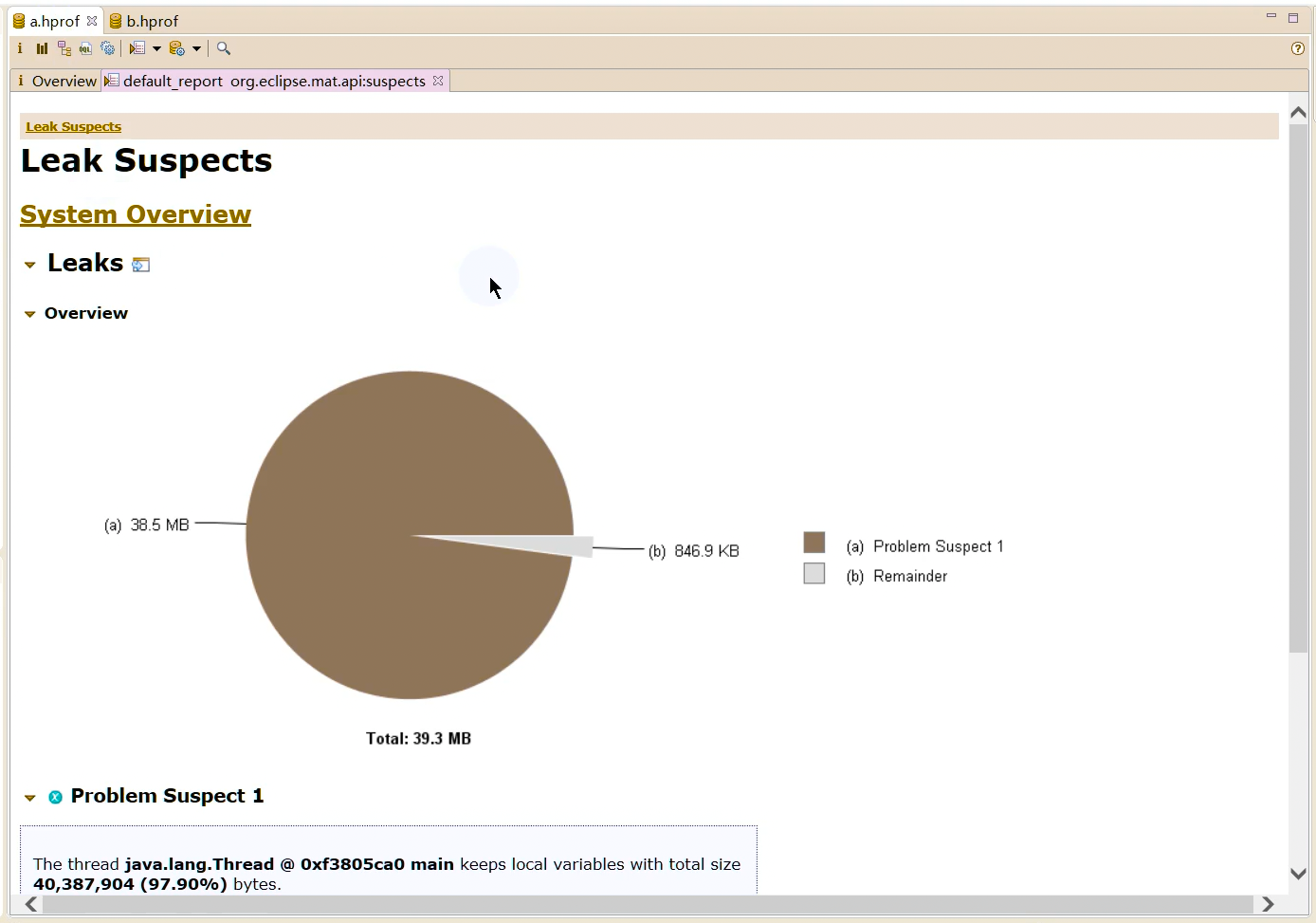
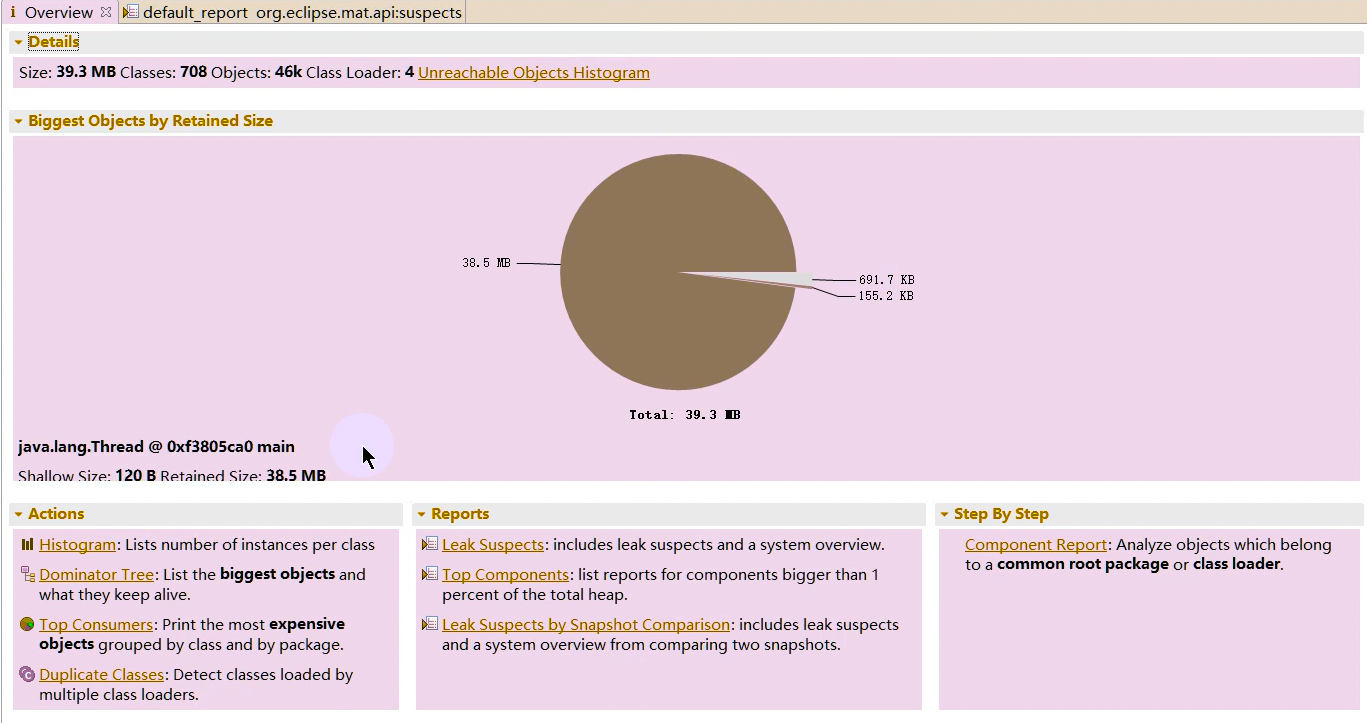
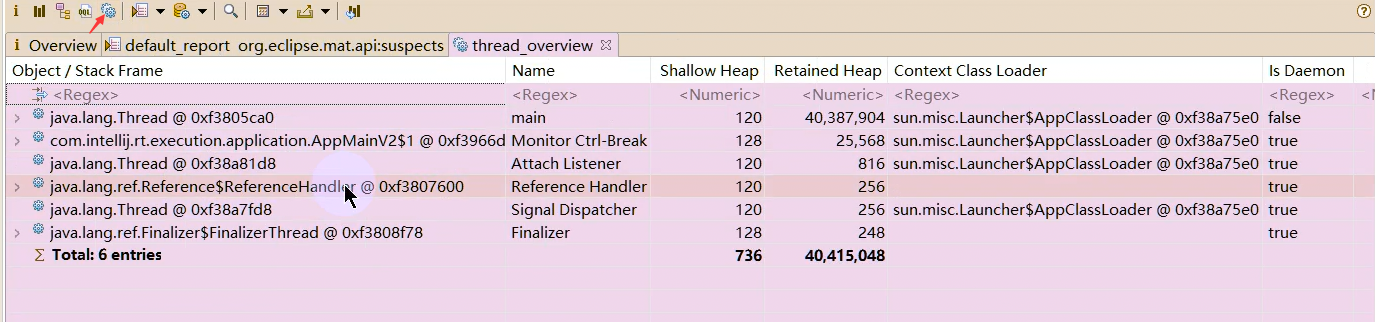
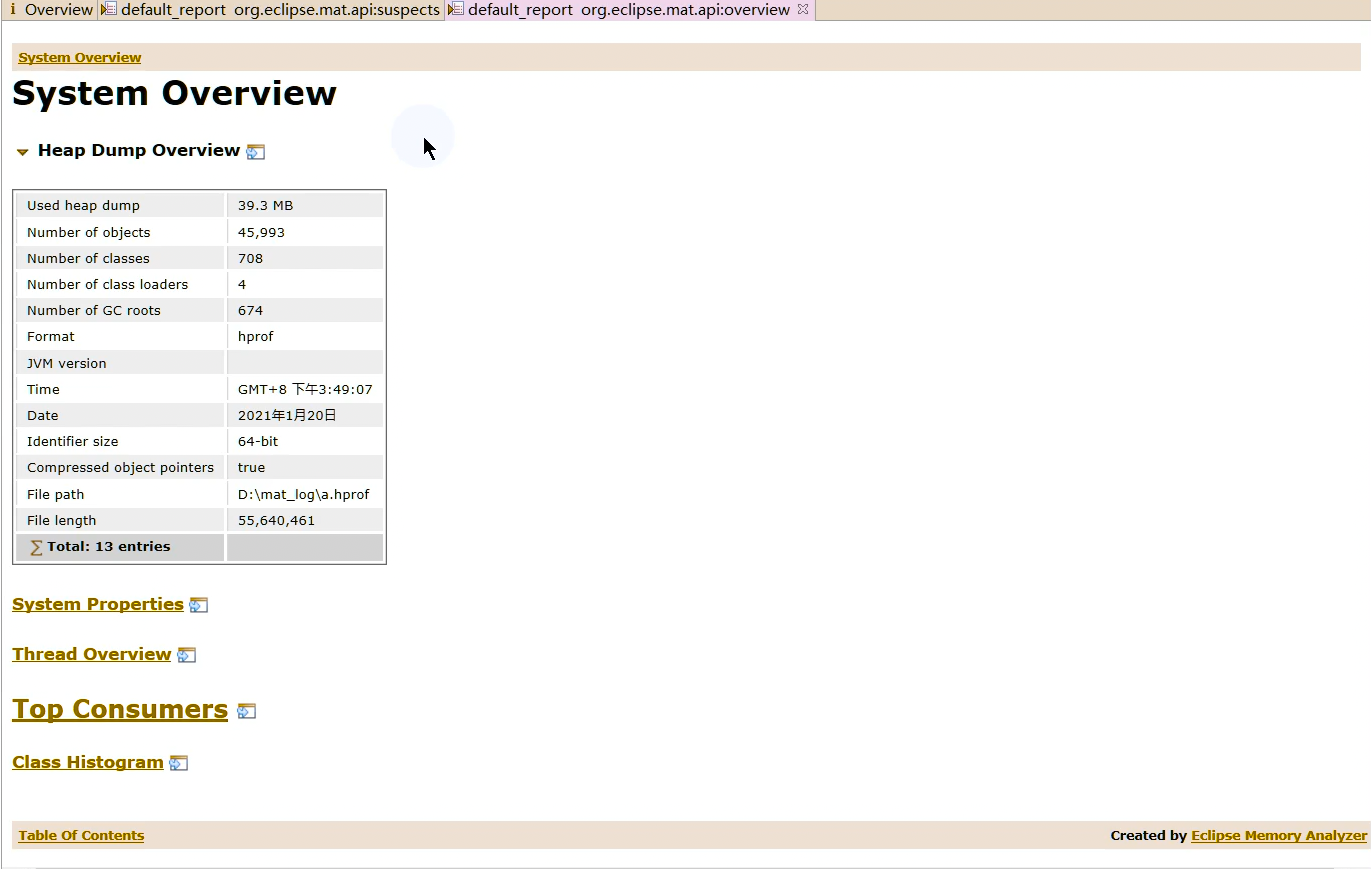
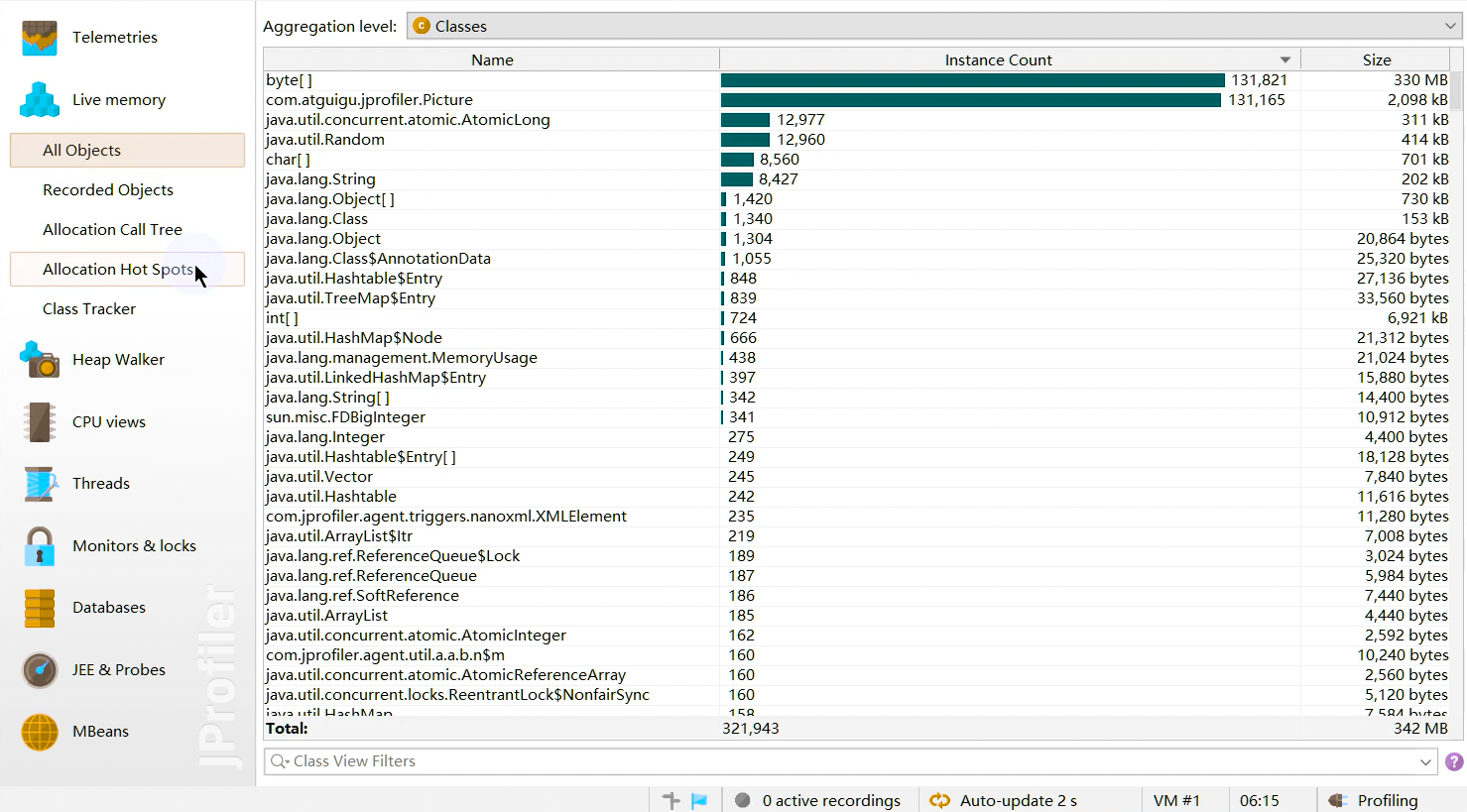
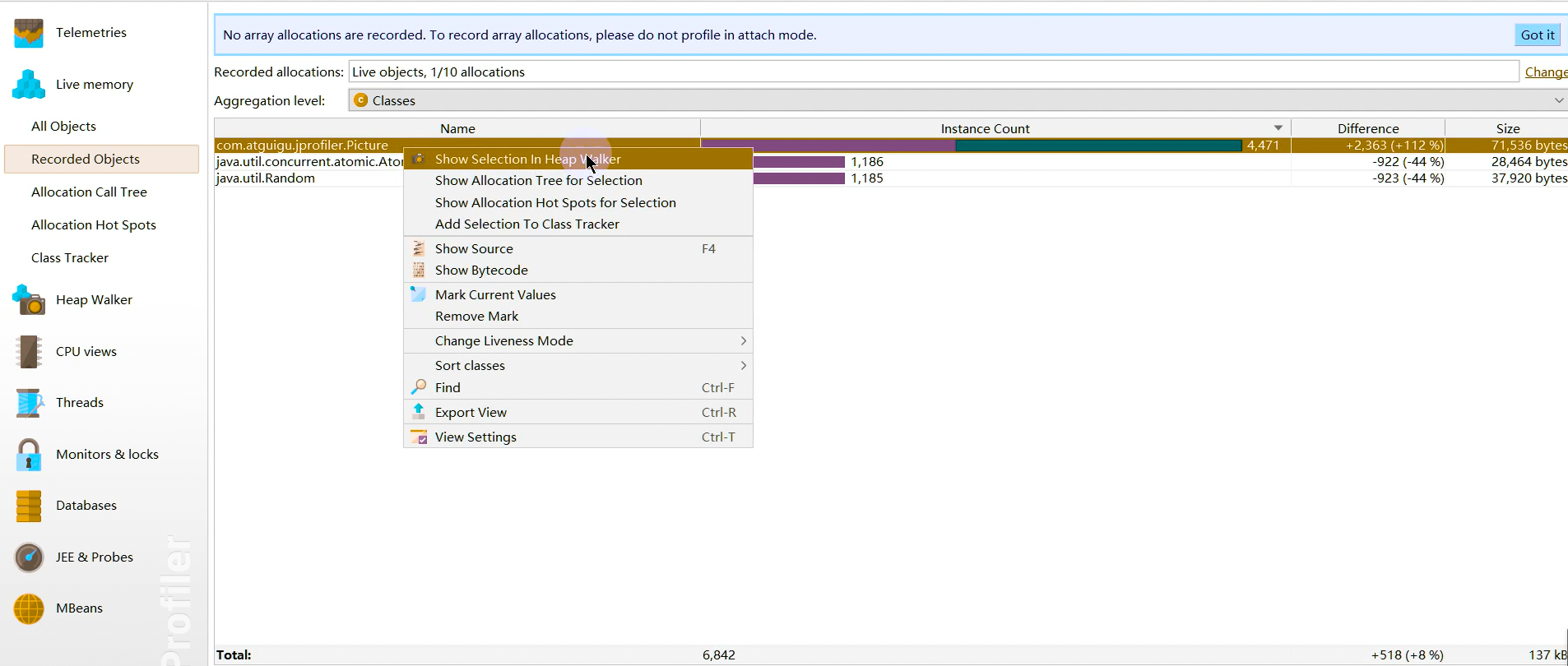
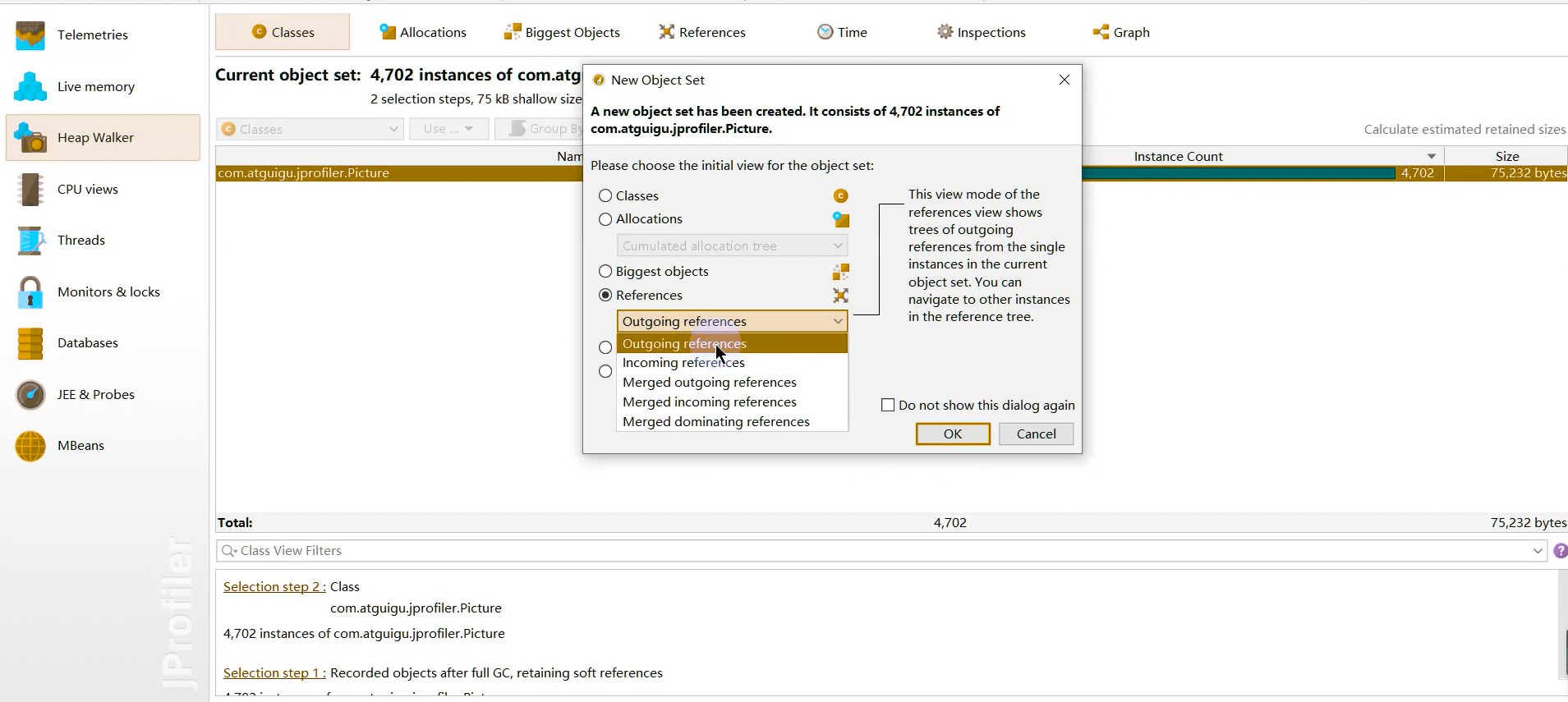
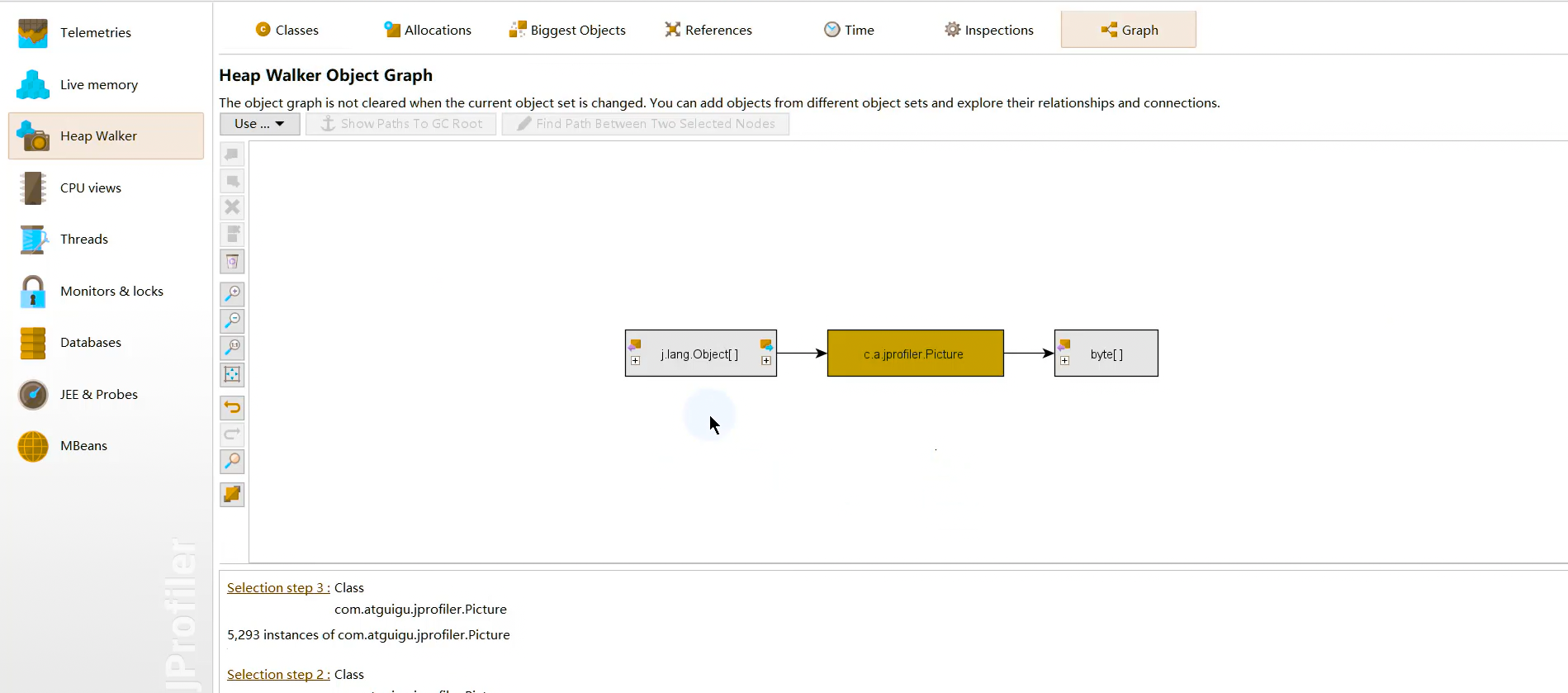
1 2 Netty is an asynchronous event-driven network application framework for rapid development of maintainable high performance protocol servers & clients.
Netty 是一个异步的、基于事件驱动的网络应用框架,用于快速开发可维护、高性能的网络服务器和客户端
解析:
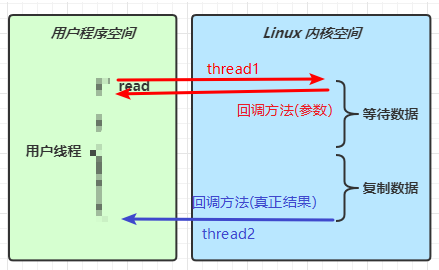
【 这里的异步 ( 并不是异步io,netty没有采用异步io ), 主要指的是netty采用多线程来完成一些方法调用和处理结果相分离,你调用方法的线程如果跟处理结果的线程是同一个,那就意味着阻塞、同步,二如果调用方法的线程和处理结果的线程是两个,那就是异步,就可以解放调用方法的线程,让调用方法的线程能腾出手来去干其它的工作。
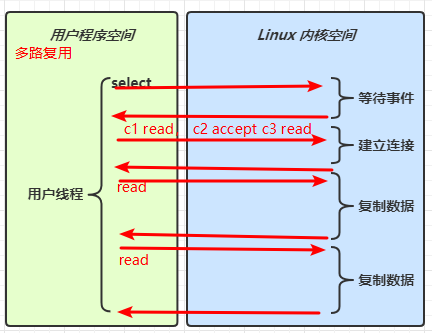
基于事件驱动 ,就是netty的底层实现是采用的多路复用技术,也就是Selector,它在io发生时才会进行相应的处理,比如可连接、可读、可写 这些事件发生时,netty才会基于这些事件来进行处理 )】
他还是另一个著名网络应用框架 Mina 的重要贡献者
Netty 在 Java 网络应用框架中的地位就好比:Spring 框架在 JavaEE 开发中的地位
以下的框架都使用了 Netty,因为它们有网络通信需求!
Cassandra - nosql 数据库
Spark - 大数据分布式计算框架
Hadoop - 大数据分布式存储框架
RocketMQ - ali 开源的消息队列
ElasticSearch - 搜索引擎
gRPC - rpc 框架
Dubbo - rpc 框架
Spring 5.x - flux api 完全抛弃了 tomcat ,使用 netty 作为服务器端
Zookeeper - 分布式协调框架
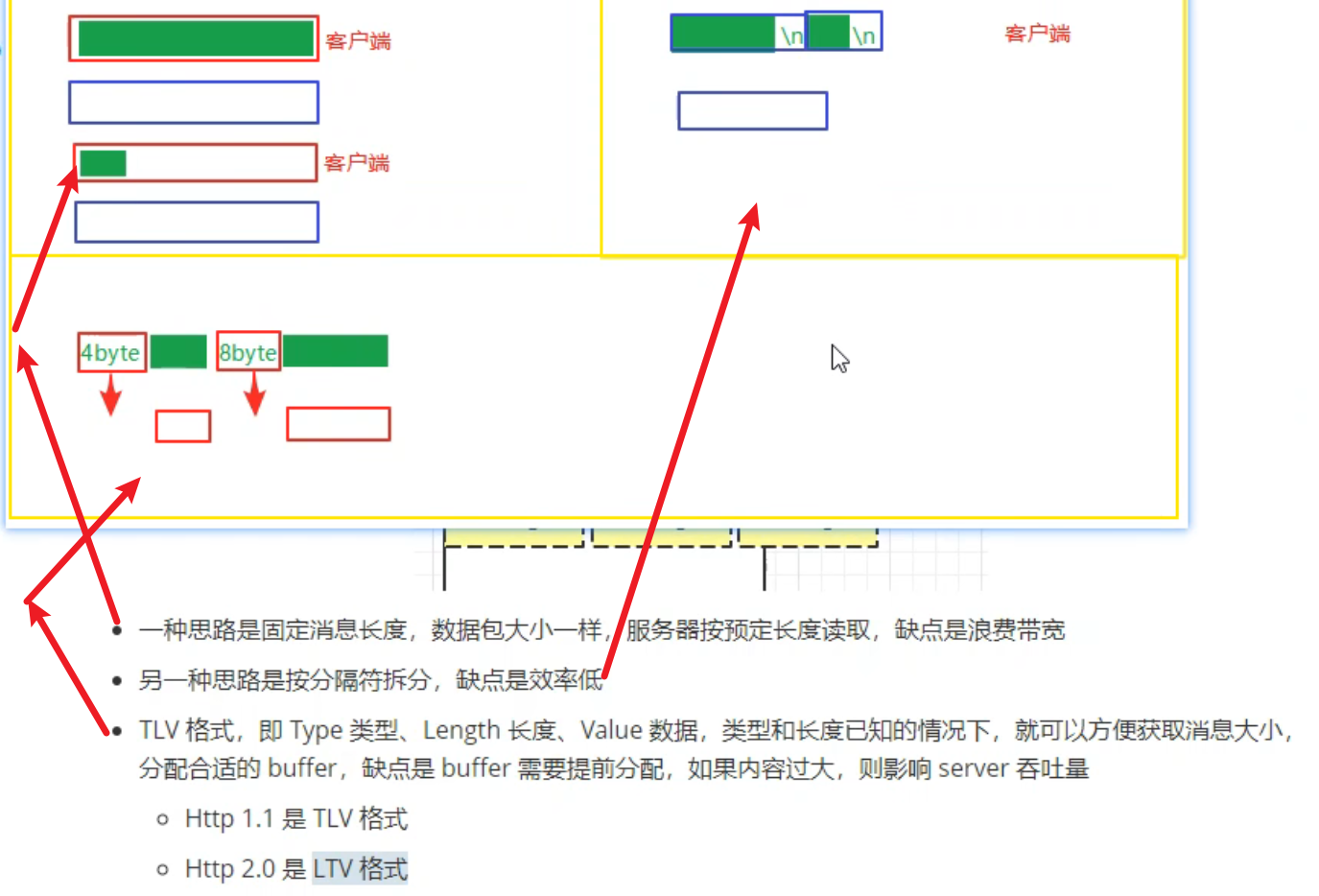
Netty vs NIO,工作量大,bug 多
需要自己构建协议
解决 TCP 传输问题,如粘包、半包
epoll 空轮询导致 CPU 100%
对 API 进行增强,使之更易用,如 FastThreadLocal => ThreadLocal,ByteBuf => ByteBuffer
Netty vs 其它网络应用框架
Mina 由 apache 维护,将来 3.x 版本可能会有较大重构,破坏 API 向下兼容性,Netty 的开发迭代更迅速,API 更简洁、文档更优秀
久经考验,有16年了,Netty 版本
2.x 2004
3.x 2008
4.x 2013
5.x 已废弃(没有明显的性能提升,维护成本高)
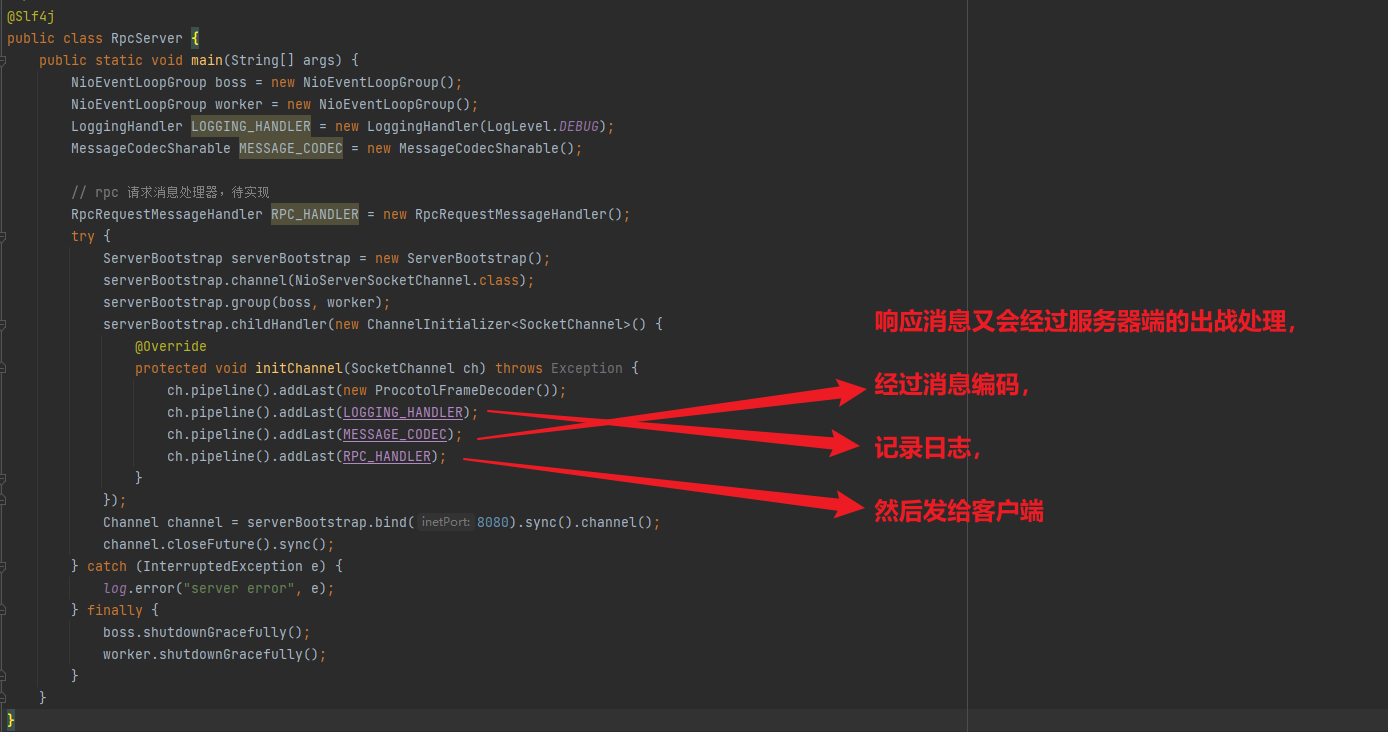
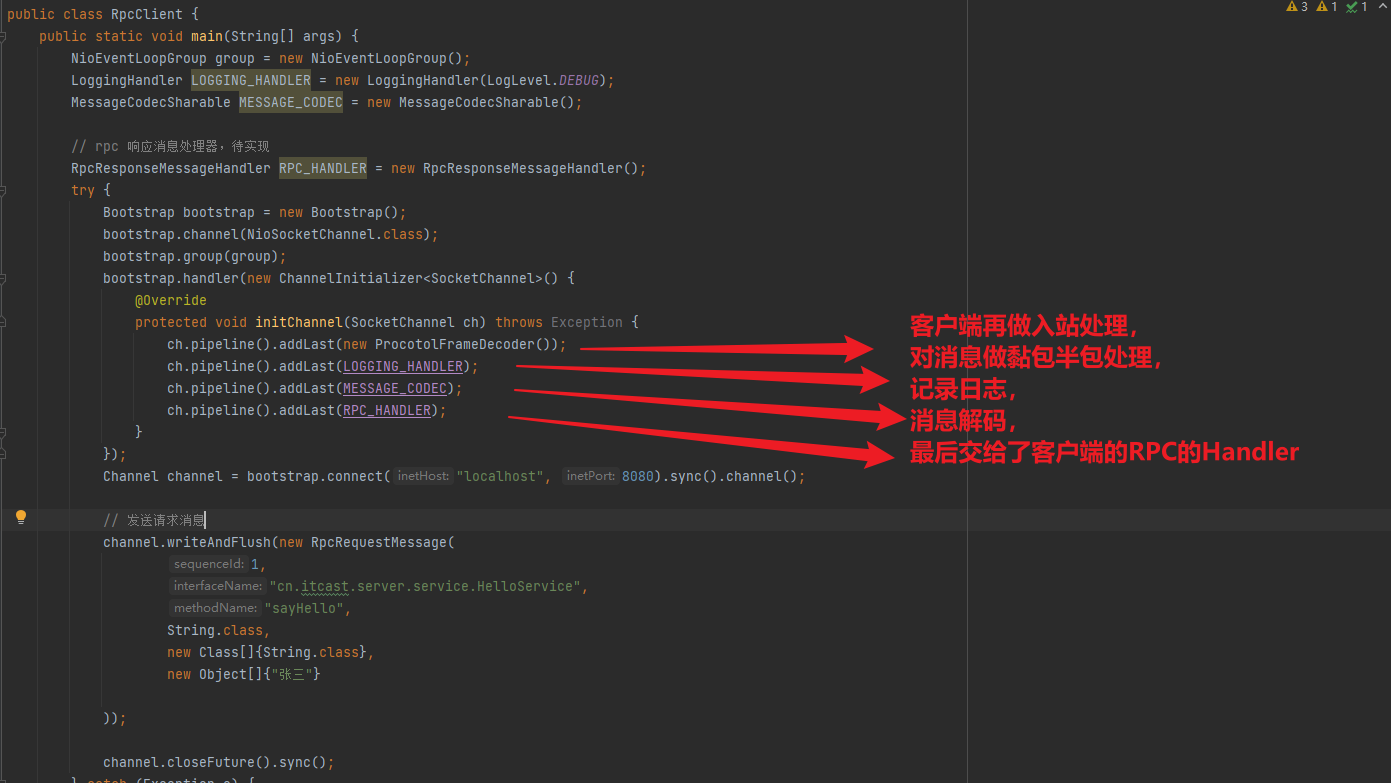
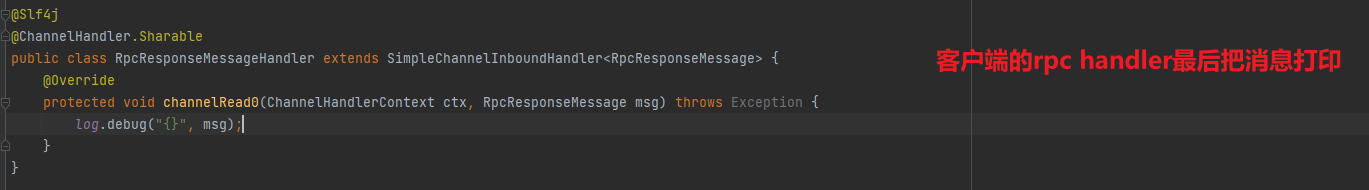
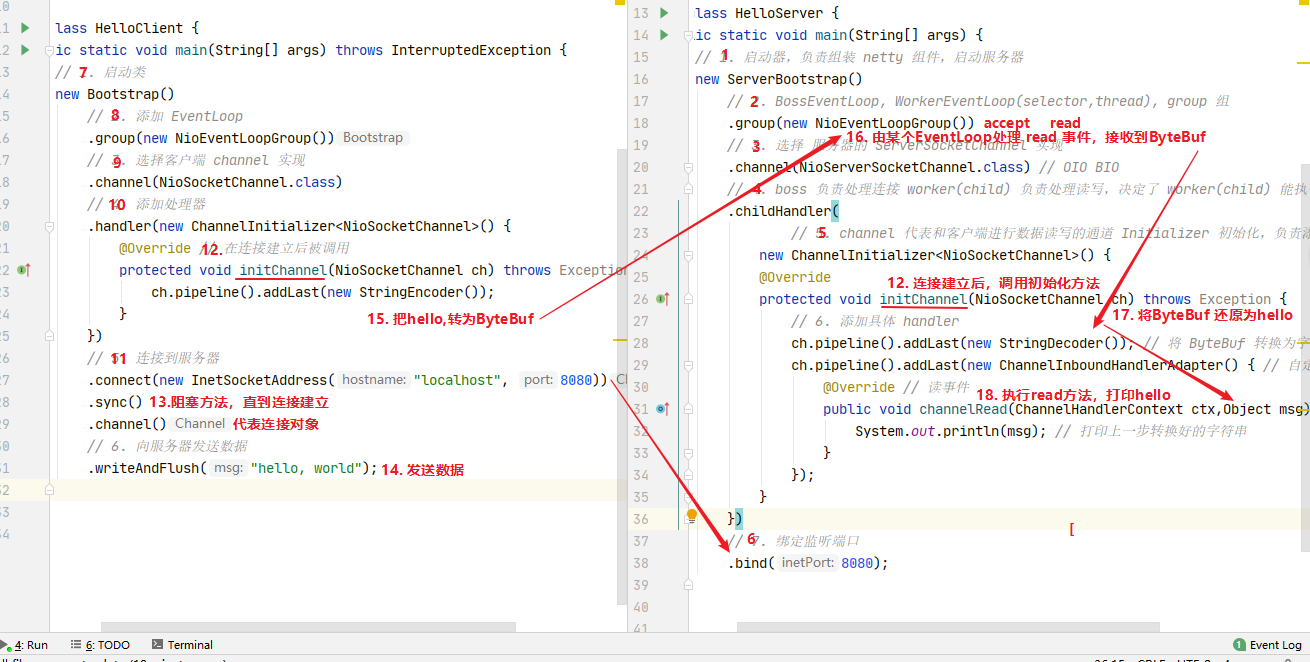
开发一个简单的服务器端和客户端
客户端向服务器端发送 hello, world
服务器仅接收,不返回
加入依赖
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > io.netty</groupId > <artifactId > netty-all</artifactId > <version > 4.1.39.Final</version > </dependency >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;public class HelloServer { public static void main (String[] args) { new ServerBootstrap () .group(new NioEventLoopGroup ()) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler( new ChannelInitializer <NioSocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (NioSocketChannel nioSocketChannel) throws Exception { nioSocketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder ()); nioSocketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter () { @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception{ System.out.println(msg); } }); } }) .bind(8080 ); } }
代码解读
1 处,创建 NioEventLoopGroup,可以简单理解为 线程池 + Selector 后面会详细展开
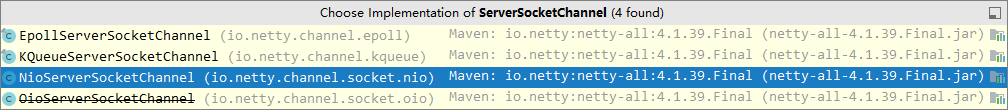
2 处,选择服务 Scoket 实现类,其中 NioServerSocketChannel 表示基于 NIO 的服务器端实现,其它实现还有
3 处,为啥方法叫 childHandler,是接下来添加的处理器都是给 SocketChannel 用的,而不是给 ServerSocketChannel。ChannelInitializer 处理器(仅执行一次),它的作用是待客户端 SocketChannel 建立连接后,执行 initChannel 以便添加更多的处理器
4 处,ServerSocketChannel 绑定的监听端口
5 处,SocketChannel 的处理器,解码 ByteBuf => String
6 处,SocketChannel 的业务处理器,使用上一个处理器的处理结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public class HelloClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { new Bootstrap () .group(new NioEventLoopGroup ()) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer <NioSocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (NioSocketChannel nioSocketChannel) throws Exception { nioSocketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder ()); } }) .connect(new InetSocketAddress ("localhost" , 8080 )) .sync() .channel() .writeAndFlush("hello, world" ); } }
代码解读
1 处,创建 NioEventLoopGroup,同 Server
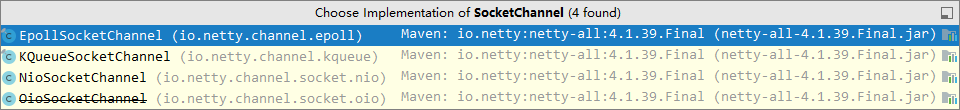
2 处,选择客户 Socket 实现类,NioSocketChannel 表示基于 NIO 的客户端实现,其它实现还有
3 处,添加 SocketChannel 的处理器,ChannelInitializer 处理器(仅执行一次),它的作用是待客户端 SocketChannel 建立连接后,执行 initChannel 以便添加更多的处理器
4 处,指定要连接的服务器和端口
5 处,Netty 中很多方法都是异步的,如 connect,这时需要使用 sync 方法等待 connect 建立连接完毕
6 处,获取 channel 对象,它即为通道抽象,可以进行数据读写操作
7 处,写入消息并清空缓冲区
8 处,消息会经过通道 handler 处理,这里是将 String => ByteBuf 发出
数据经过网络传输,到达服务器端,服务器端 5 和 6 处的 handler 先后被触发,走完一个流程
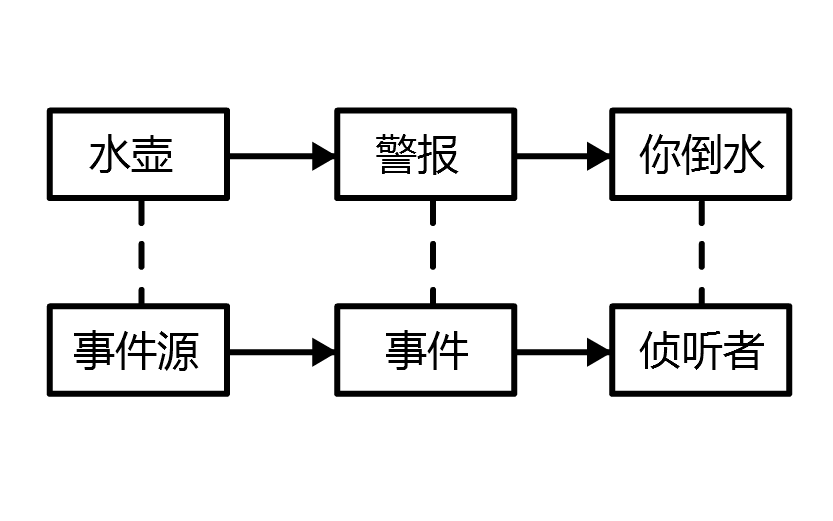
一开始需要树立正确的观念
把 channel 理解为数据的通道
把 msg 理解为流动的数据,最开始输入是 ByteBuf,但经过 pipeline 的加工,会变成其它类型对象,最后输出又变成 ByteBuf
把 handler 理解为数据的处理工序
工序有多道,合在一起就是 pipeline,pipeline 负责发布事件(读、读取完成…)传播给每个 handler, handler 对自己感兴趣的事件进行处理(重写了相应事件处理方法)
handler 分 Inbound 和 Outbound 两类 ( 入站:客户端先服务器输入数据时用Inbound; 出站:数据向客户端写出时用Outbound )
把 eventLoop 理解为处理数据的工人
工人可以管理多个 channel 的 io 操作,并且一旦工人负责了某个 channel,就要负责到底(绑定)
工人既可以执行 io 操作,也可以进行任务处理,每位工人有任务队列,队列里可以堆放多个 channel 的待处理任务,任务分为普通任务、定时任务
工人按照 pipeline 顺序,依次按照 handler 的规划(代码)处理数据,可以为每道工序指定不同的工人
事件循环对象
EventLoop 本质是一个单线程执行器(同时维护了一个 Selector),里面有 run 方法处理 Channel 上源源不断的 io 事件。
它的继承关系比较复杂
一条线是继承自 j.u.c.ScheduledExecutorService 因此包含了线程池中所有的方法
另一条线是继承自 netty 自己的 OrderedEventExecutor,
提供了 boolean inEventLoop(Thread thread) 方法判断一个线程是否属于此 EventLoop
提供了 parent 方法来看看自己属于哪个 EventLoopGroup
事件循环组
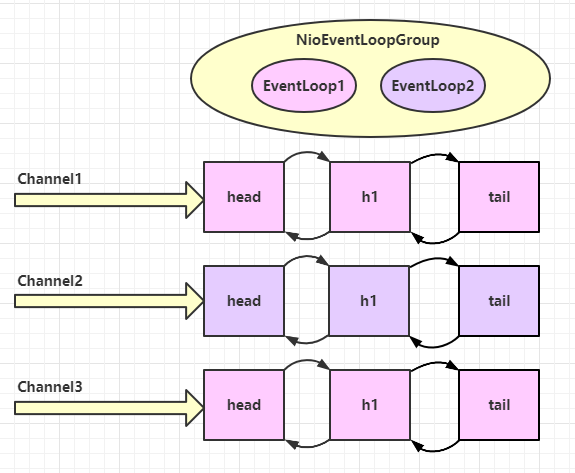
EventLoopGroup 是一组 EventLoop,Channel 一般会调用 EventLoopGroup 的 register 方法来绑定其中一个 EventLoop,后续这个 Channel 上的 io 事件都由此 EventLoop 来处理(保证了 io 事件处理时的线程安全)
继承自 netty 自己的 EventExecutorGroup
实现了 Iterable 接口提供遍历 EventLoop 的能力
另有 next 方法获取集合中下一个 EventLoop
以一个简单的实现为例:
1 2 3 4 5 DefaultEventLoopGroup group = new DefaultEventLoopGroup (2 );System.out.println(group.next()); System.out.println(group.next()); System.out.println(group.next());
输出
1 2 3 io.netty.channel.DefaultEventLoop@60f82f98 io.netty.channel.DefaultEventLoop@35f983a6 io.netty.channel.DefaultEventLoop@60f82f98
也可以使用 for 循环
1 2 3 4 DefaultEventLoopGroup group = new DefaultEventLoopGroup (2 );for (EventExecutor eventLoop : group) { System.out.println(eventLoop); }
输出
1 2 io.netty.channel.DefaultEventLoop@60f82f98 io.netty.channel.DefaultEventLoop@35f983a6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. 创建事件循环组 如果不传参数或是参数传0,就采用默认的线程数(系统的虚拟机所在的电脑的CPU核心数*2) EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(2); // 能处理: io事件,普通事件,定时任务 // EventLoopGroup group1 = new DefaultEventLoop(); // 能处理: 普通任务,定时任务 // 2. next() 获取下一个事件循环对象 System.out.println(group.next()); System.out.println(group.next()); System.out.println(group.next()); System.out.println(group.next()); // 3. .submit() 或 .execute()执行普通任务 // 意义:一个代码的执行权需要由一个线程转移到另一个线程时 // 1) 可以进行进行业务异步处理,比如 比较耗时的任务当前线程不想完成,就可以让 EventLoopGroup 事件循环组里的线程来完成 // 2) 做一些事件分发的时候,会用到这种提交任务 group.next().submit(()->{ try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } log.info("ok"); }); log.info("main"); // 执行定时任务 // scheduleAtFixedRate 有四个参数: // 参数1:任务对象 2:初始延时时间(延时后才启动这个定时操作,0的话就表示立刻启动) 3:间隔时间 4:时间单位 group.next().scheduleAtFixedRate(()->{ log.info("okk"); }, 0, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); }
.submit() 或 .execute()执行普通任务
意义:一个代码的执行权需要由一个线程转移到另一个线程时
1) 可以进行进行业务异步处理,比如 比较耗时的任务当前线程不想完成,就可以让 EventLoopGroup 事件循环组里的线程来完成
2) 做一些事件分发的时候,会用到这种提交任务
优雅关闭 shutdownGracefully 方法。该方法会首先切换 EventLoopGroup 到关闭状态从而拒绝新的任务的加入,然后在任务队列的任务都处理完成后,停止线程的运行。从而确保整体应用是在正常有序的状态下退出的
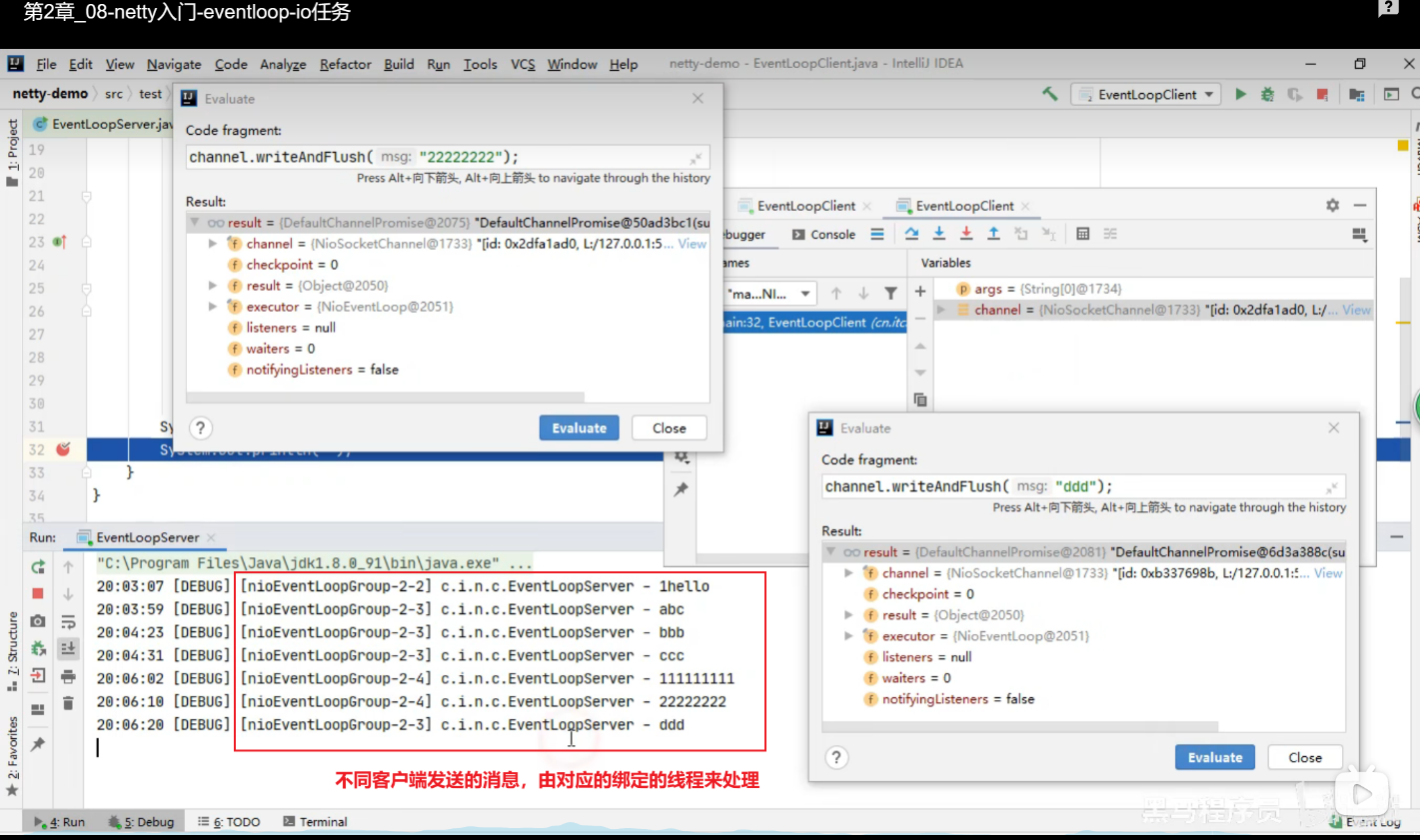
nio线程一旦连接成功,就会建立绑定关系,channel就会跟一个NioEventLoop绑定
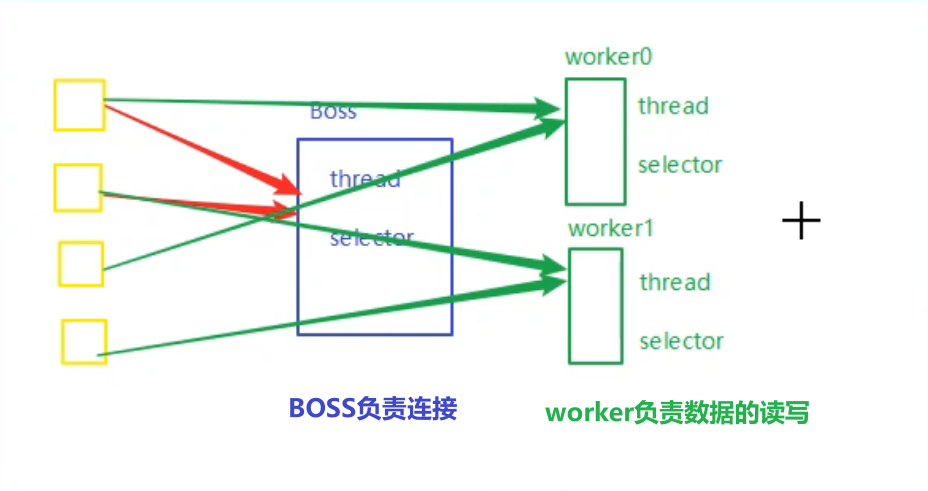
服务器端两个 nio worker 工人
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 new ServerBootstrap () .group(new NioEventLoopGroup (1 ), new NioEventLoopGroup (2 )) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer <NioSocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (NioSocketChannel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter () { @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { ByteBuf byteBuf = msg instanceof ByteBuf ? ((ByteBuf) msg) : null ; if (byteBuf != null ) { byte [] buf = new byte [16 ]; ByteBuf len = byteBuf.readBytes(buf, 0 , byteBuf.readableBytes()); log.debug(new String (buf)); } } }); } }).bind(8080 ).sync();
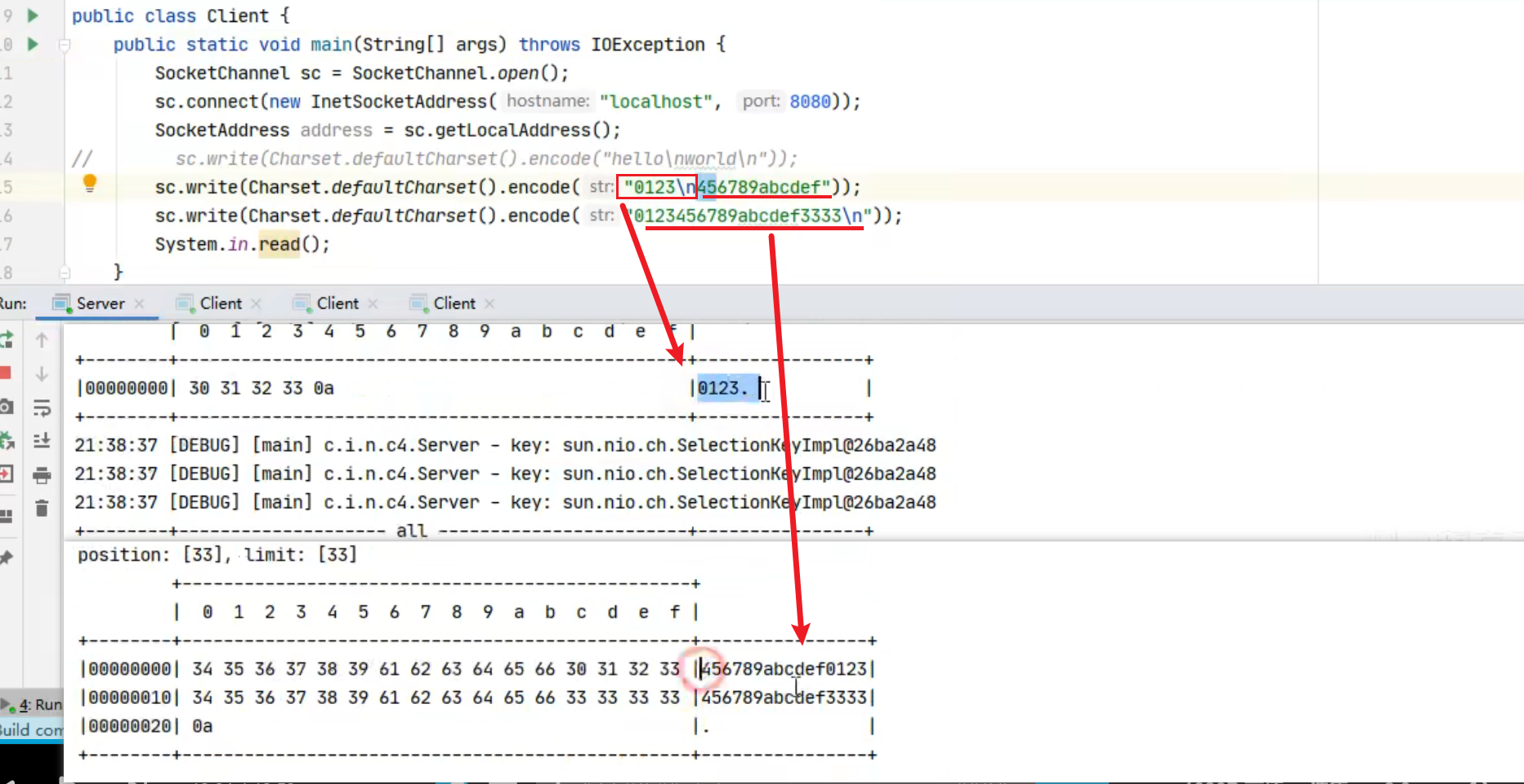
客户端,启动三次,分别修改发送字符串为 zhangsan(第一次),lisi(第二次),wangwu(第三次)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Channel channel = new Bootstrap () .group(new NioEventLoopGroup (1 )) .handler(new ChannelInitializer <NioSocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception { System.out.println("init..." ); ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.DEBUG)); } }) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class).connect("localhost" , 8080 ) .sync() .channel(); channel.writeAndFlush(ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer().writeBytes("wangwu" .getBytes())); Thread.sleep(2000 ); channel.writeAndFlush(ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer().writeBytes("wangwu" .getBytes()));
最后输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 22:03:34 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] c.i.o.EventLoopTest - zhangsan 22:03:36 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] c.i.o.EventLoopTest - zhangsan 22:05:36 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-3-2] c.i.o.EventLoopTest - lisi 22:05:38 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-3-2] c.i.o.EventLoopTest - lisi 22:06:09 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] c.i.o.EventLoopTest - wangwu 22:06:11 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-3-1] c.i.o.EventLoopTest - wangwu
可以看到两个工人轮流处理 channel,但工人与 channel 之间进行了绑定
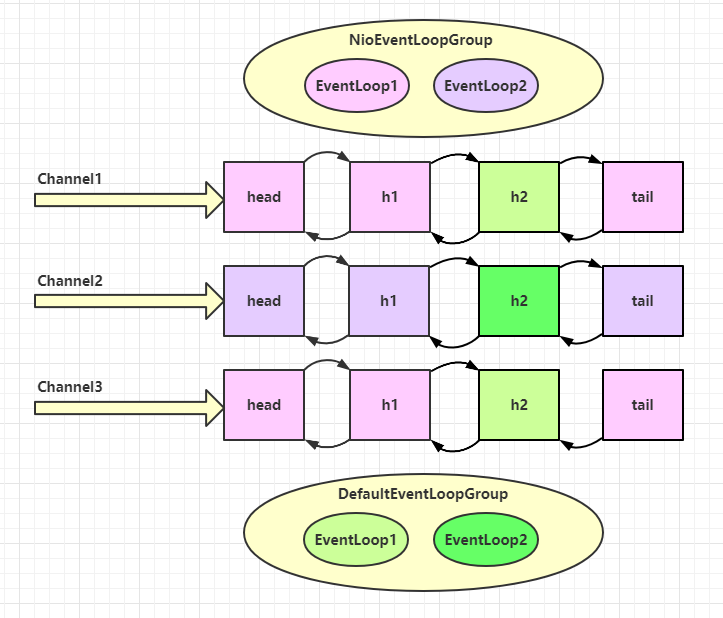
再增加两个非 nio 工人
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 DefaultEventLoopGroup normalWorkers = new DefaultEventLoopGroup (2 );new ServerBootstrap () .group(new NioEventLoopGroup (1 ), new NioEventLoopGroup (2 )) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer <NioSocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (NioSocketChannel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.DEBUG)); ch.pipeline().addLast(normalWorkers,"myhandler" , new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter () { @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { ByteBuf byteBuf = msg instanceof ByteBuf ? ((ByteBuf) msg) : null ; if (byteBuf != null ) { byte [] buf = new byte [16 ]; ByteBuf len = byteBuf.readBytes(buf, 0 , byteBuf.readableBytes()); log.debug(new String (buf)); } } }); } }).bind(8080 ).sync();
客户端代码不变,启动三次,分别修改发送字符串为 zhangsan(第一次),lisi(第二次),wangwu(第三次)
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 22:19:48 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-1] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x251562d5, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52588] REGISTERED 22:19:48 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-1] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x251562d5, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52588] ACTIVE 22:19:48 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-1] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x251562d5, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52588] READ: 8B +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 7a 68 61 6e 67 73 61 6e |zhangsan | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ 22:19:48 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-1] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x251562d5, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52588] READ COMPLETE 22:19:48 [DEBUG] [defaultEventLoopGroup-2-1] c.i.o.EventLoopTest - zhangsan 22:19:50 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-1] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x251562d5, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52588] READ: 8B +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 7a 68 61 6e 67 73 61 6e |zhangsan | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ 22:19:50 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-1] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x251562d5, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52588] READ COMPLETE 22:19:50 [DEBUG] [defaultEventLoopGroup-2-1] c.i.o.EventLoopTest - zhangsan 22:20:24 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-2] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x94b2a840, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52612] REGISTERED 22:20:24 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-2] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x94b2a840, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52612] ACTIVE 22:20:25 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-2] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x94b2a840, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52612] READ: 4B +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 6c 69 73 69 |lisi | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ 22:20:25 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-2] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x94b2a840, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52612] READ COMPLETE 22:20:25 [DEBUG] [defaultEventLoopGroup-2-2] c.i.o.EventLoopTest - lisi 22:20:27 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-2] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x94b2a840, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52612] READ: 4B +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 6c 69 73 69 |lisi | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ 22:20:27 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-2] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x94b2a840, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52612] READ COMPLETE 22:20:27 [DEBUG] [defaultEventLoopGroup-2-2] c.i.o.EventLoopTest - lisi 22:20:38 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-1] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x79a26af9, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52625] REGISTERED 22:20:38 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-1] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x79a26af9, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52625] ACTIVE 22:20:38 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-1] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x79a26af9, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52625] READ: 6B +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 77 61 6e 67 77 75 |wangwu | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ 22:20:38 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-1] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x79a26af9, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52625] READ COMPLETE 22:20:38 [DEBUG] [defaultEventLoopGroup-2-1] c.i.o.EventLoopTest - wangwu 22:20:40 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-1] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x79a26af9, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52625] READ: 6B +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 77 61 6e 67 77 75 |wangwu | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ 22:20:40 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-4-1] i.n.h.l.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x79a26af9, L:/127.0.0.1:8080 - R:/127.0.0.1:52625] READ COMPLETE 22:20:40 [DEBUG] [defaultEventLoopGroup-2-1] c.i.o.EventLoopTest - wangwu
可以看到,nio 工人和 非 nio 工人也分别绑定了 channel(LoggingHandler 由 nio 工人执行,而我们自己的 handler 由非 nio 工人执行)
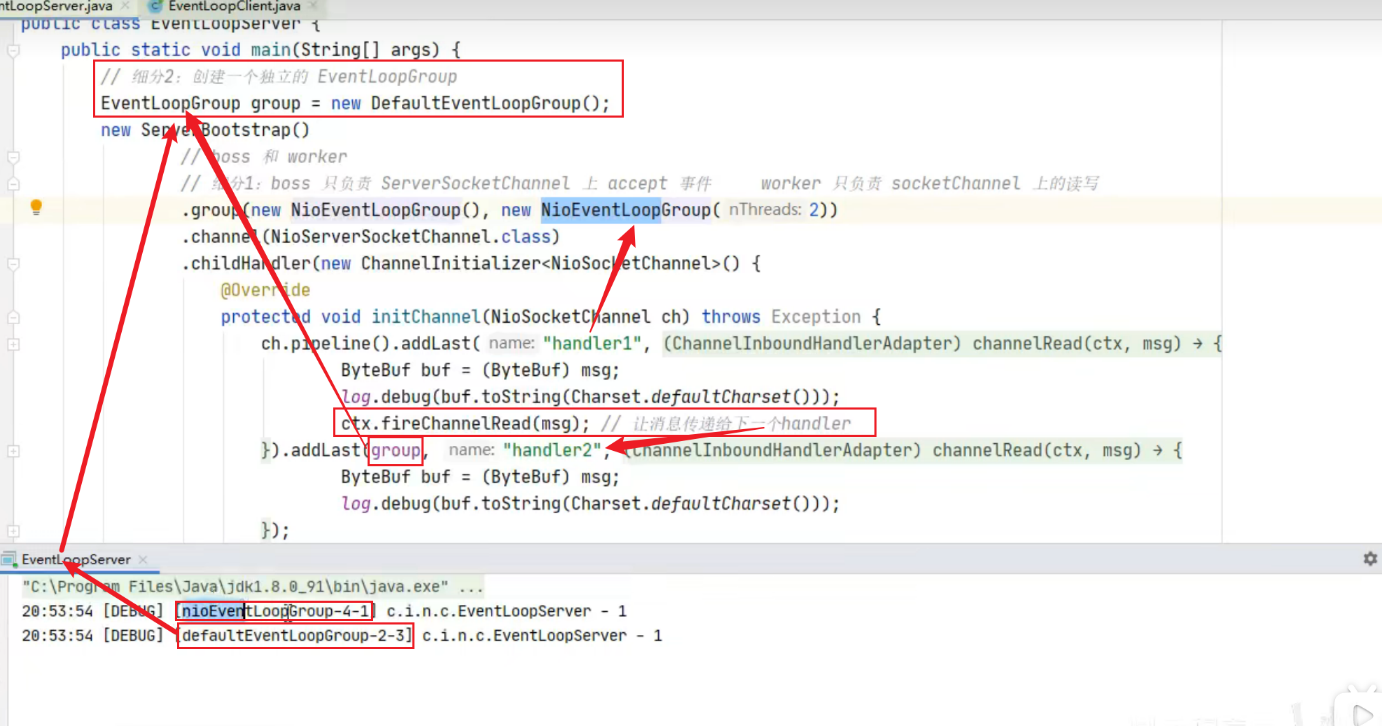
EvenLoop细分1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 DefaultEventLoopGroup normalWorkers = new DefaultEventLoopGroup (2 );new ServerBootstrap () .group(new NioEventLoopGroup (1 ), new NioEventLoopGroup (2 )) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer <NioSocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (NioSocketChannel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.DEBUG)); ch.pipeline().addLast(normalWorkers,"myhandler" , new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter () { @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { ByteBuf byteBuf = msg instanceof ByteBuf ? ((ByteBuf) msg) : null ; if (byteBuf != null ) { byte [] buf = new byte [16 ]; ByteBuf len = byteBuf.readBytes(buf, 0 , byteBuf.readableBytes()); log.debug(new String (buf)); } } }); } }).bind(8080 ).sync();
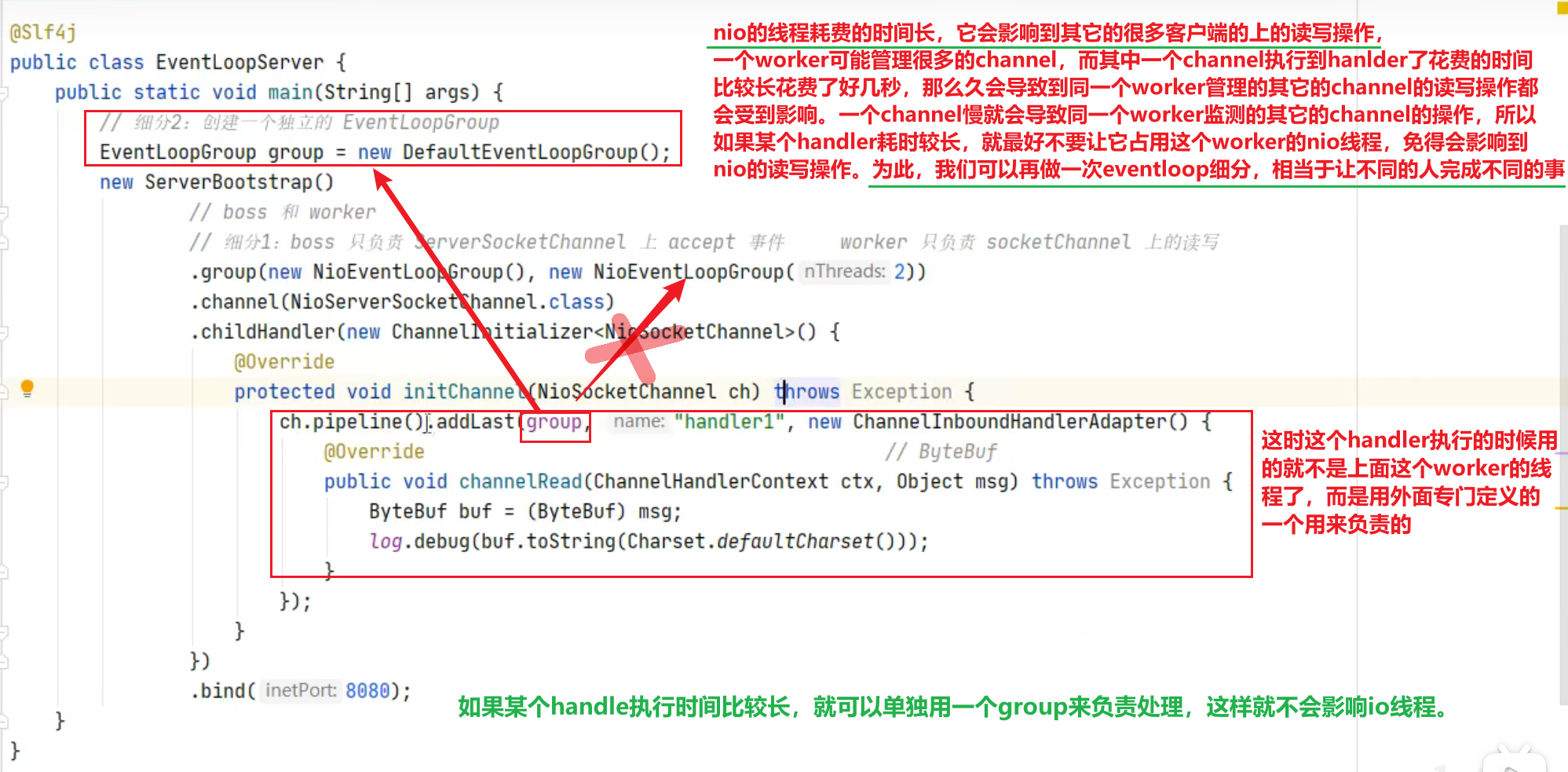
为什么要做EvenLoop的细分2?
nio的线程耗费的时间长,它会影响到其它的很多客户端的上的读写操作,一个worker可能管理很多的channel,而其中一个channel执行到hanlder了花费的时间的比较长花费了好几秒,那么久会导致到同一个worker管理的其它的channel的读写操作都会受到影响。一个channel满就会导致同一个worker检测的其它的channel的操作,所以如果某个handler耗时较长,就最好不要让它占用这个worker的nio线程,免得会影响到nio的读写操作。为此,我们可以再做一次eventloop细分,相当于让不同的人完成不同的事。(如果某个handle执行时间比较长,就可以单独用一个group来负责处理,这样就不会影响io线程。)
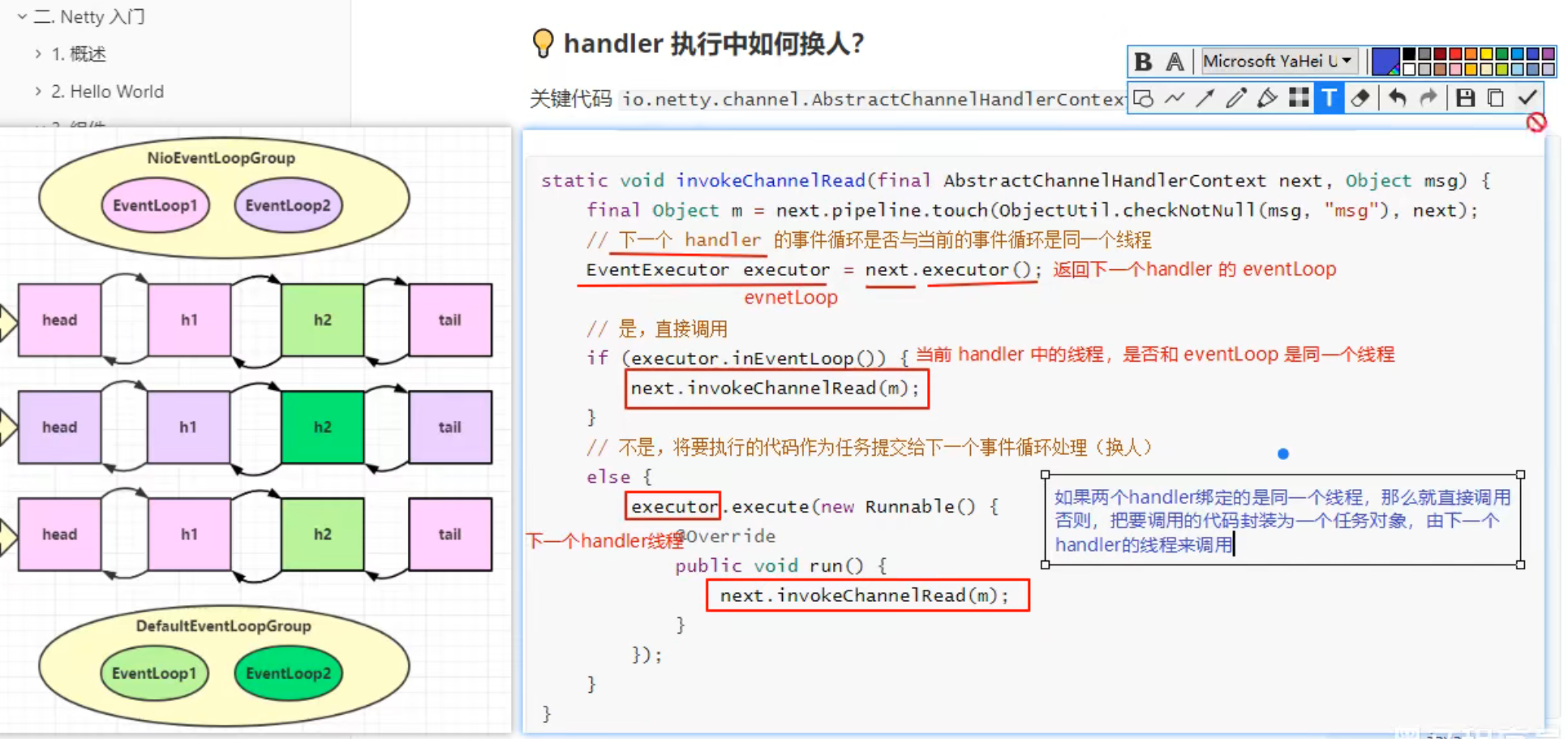
两个handler,前一个handler消息处理完后就传给下一个handler处理,但前一个如果不执行 .fireChannelRead(msg) 的话,后面的handler就不能继续处理了
关键代码 io.netty.channel.AbstractChannelHandlerContext#invokeChannelRead()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 static void invokeChannelRead (final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg) { final Object m = next.pipeline.touch(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(msg, "msg" ), next); EventExecutor executor = next.executor(); if (executor.inEventLoop()) { next.invokeChannelRead(m); } else { executor.execute(new Runnable () { @Override public void run () { next.invokeChannelRead(m); } }); } }
如果两个 handler 绑定的是同一个线程,那么就直接调用
否则,把要调用的代码封装为一个任务对象,由下一个 handler 的线程来调用
NioEventLoop 除了可以处理 io 事件,同样可以向它提交普通任务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 NioEventLoopGroup nioWorkers = new NioEventLoopGroup (2 );log.debug("server start..." ); Thread.sleep(2000 ); nioWorkers.execute(()->{ log.debug("normal task..." ); });
输出
1 2 22:30:36 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.o.EventLoopTest2 - server start... 22:30:38 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] c.i.o.EventLoopTest2 - normal task...
可以用来执行耗时较长的任务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 NioEventLoopGroup nioWorkers = new NioEventLoopGroup (2 );log.debug("server start..." ); Thread.sleep(2000 ); nioWorkers.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> { log.debug("running..." ); }, 0 , 1 , TimeUnit.SECONDS);
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 22:35:15 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.o.EventLoopTest2 - server start... 22:35:17 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] c.i.o.EventLoopTest2 - running... 22:35:18 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] c.i.o.EventLoopTest2 - running... 22:35:19 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] c.i.o.EventLoopTest2 - running... 22:35:20 [DEBUG] [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] c.i.o.EventLoopTest2 - running... ...
可以用来执行定时任务
channel 的主要作用
close() 可以用来关闭 channel
closeFuture() 用来处理 channel 的关闭
sync 方法作用是同步等待 channel 关闭
而 addListener 方法是异步等待 channel 关闭
pipeline() 方法添加处理器
write() 方法将数据写入 (存在缓冲区中,不会直接刷出,后面要执行flush将缓冲区的数据刷出,或是等到缓冲区积累到一定数量时才会自动一次性刷出)
writeAndFlush() 方法将数据写入并刷出 (写入缓冲区后就立刻刷出)
这时刚才的客户端代码
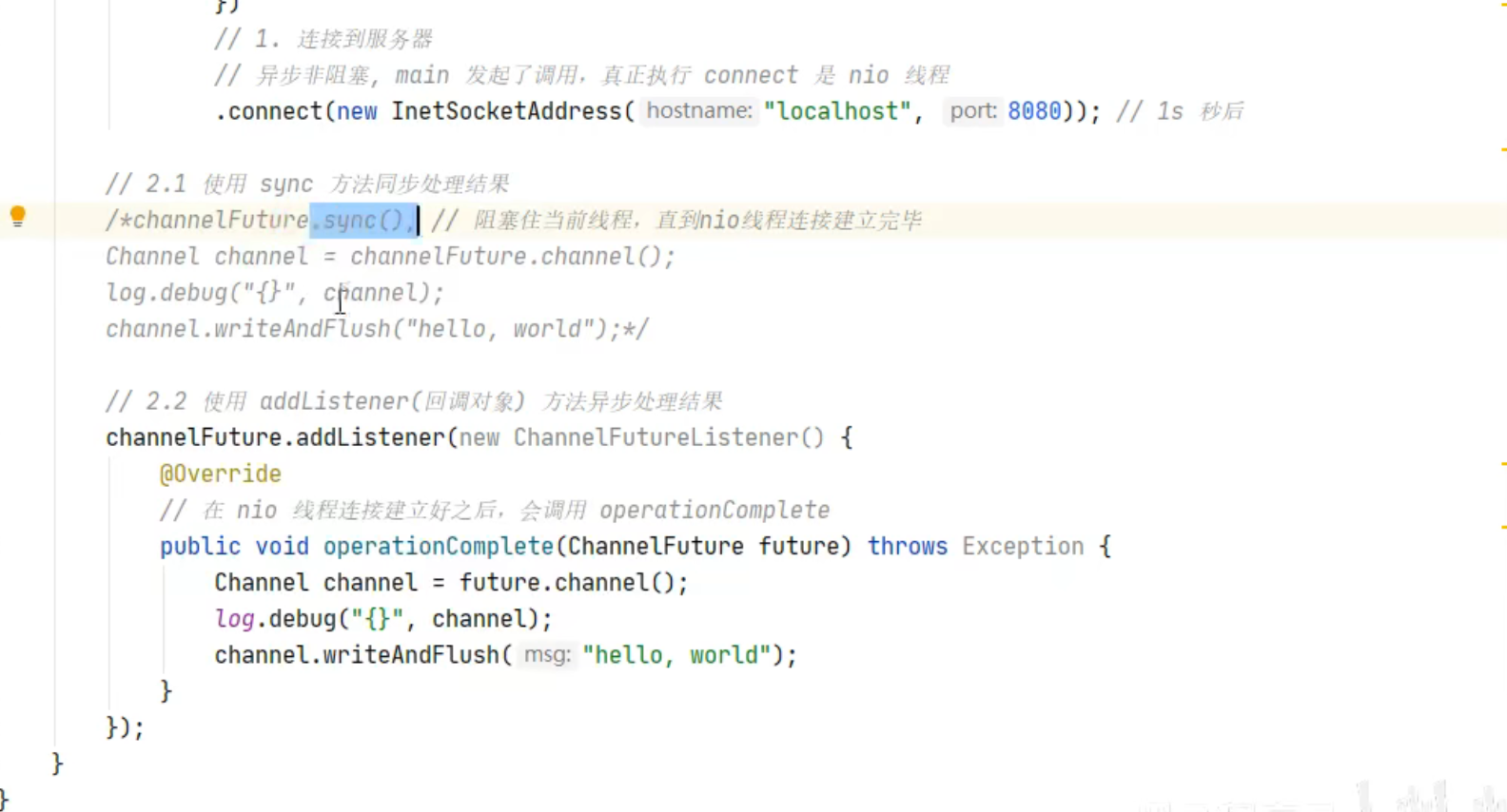
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 new Bootstrap () .group(new NioEventLoopGroup ()) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer <Channel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (Channel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder ()); } }) .connect("127.0.0.1" , 8080 ) .sync() .channel() .writeAndFlush(new Date () + ": hello world!" );
现在把它拆开来看
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap () .group(new NioEventLoopGroup ()) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer <Channel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (Channel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder ()); } }) .connect("127.0.0.1" , 8080 ); channelFuture.sync().channel().writeAndFlush(new Date () + ": hello world!" );
1 处返回的是 ChannelFuture 对象,它的作用是利用 channel() 方法来获取 Channel 对象
注意 connect 方法是异步的 ,意味着不等连接建立,方法执行就返回了。因此 channelFuture 对象中不能【立刻】获得到正确的 Channel 对象
实验如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap () .group(new NioEventLoopGroup ()) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer <Channel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (Channel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder ()); } }) .connect("127.0.0.1" , 8080 ); System.out.println(channelFuture.channel()); channelFuture.sync(); System.out.println(channelFuture.channel());
执行到 1 时,连接未建立,打印 [id: 0x2e1884dd]
执行到 2 时,sync 方法是同步等待连接建立完成
执行到 3 时,连接肯定建立了,打印 [id: 0x2e1884dd, L:/127.0.0.1:57191 - R:/127.0.0.1:8080]
除了用 sync 方法可以让异步操作同步 以外,还可以使用回调的方式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap () .group(new NioEventLoopGroup ()) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer <Channel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (Channel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder ()); } }) .connect("127.0.0.1" , 8080 ); System.out.println(channelFuture.channel()); channelFuture.addListener((ChannelFutureListener) future -> { System.out.println(future.channel()); });
执行到 1 时,连接未建立,打印 [id: 0x749124ba]
ChannelFutureListener 会在连接建立时被调用(其中 operationComplete 方法),因此执行到 2 时,连接肯定建立了,打印 [id: 0x749124ba, L:/127.0.0.1:57351 - R:/127.0.0.1:8080]
ps: 带有 Future,promise的类型都是和异步方法配套使用的,用来处理结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 @Slf4j public class CloseFutureClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { NioEventLoopGroup group new NioEventLoopGroup (); ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap () .group(group) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer <NioSocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.DEBUG)); ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder ()); } }) .connect(new InetSocketAddress ("localhost" , 8080 )); Channel channel = channelFuture.sync().channel(); log.debug("{}" , channel); new Thread (()->{ Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); while (true ) { String line = scanner.nextLine(); if ("q" .equals(line)) { channel.close(); break ; } channel.writeAndFlush(line); } }, "input" ).start(); ChannelFuture closeFuture = channel.closeFuture(); closeFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener () { @Override public void operationComplete (ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { log.debug("处理关闭之后的操作" ); group.shutdownGracefully(); } }); } }
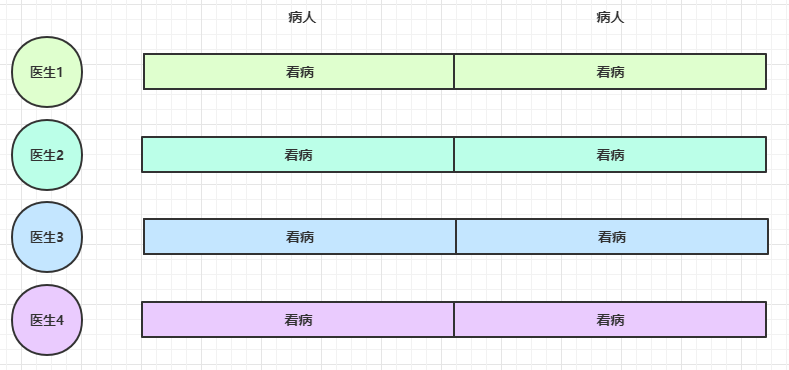
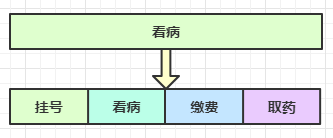
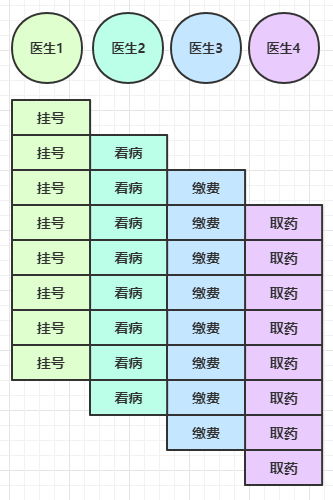
思考下面的场景,4 个医生给人看病,每个病人花费 20 分钟,而且医生看病的过程中是以病人为单位的,一个病人看完了,才能看下一个病人。假设病人源源不断地来,可以计算一下 4 个医生一天工作 8 小时,处理的病人总数是:4 * 8 * 3 = 96
经研究发现,看病可以细分为四个步骤,经拆分后每个步骤需要 5 分钟,如下
因此可以做如下优化,只有一开始,医生 2、3、4 分别要等待 5、10、15 分钟才能执行工作,但只要后续病人源源不断地来,他们就能够满负荷工作,并且处理病人的能力提高到了 4 * 8 * 12 效率几乎是原来的四倍
要点
单线程没法异步提高效率,必须配合多线程、多核 cpu 才能发挥异步的优势
异步并没有缩短响应时间,反而有所增加;这里异步提高的是吞吐量,提高单位时间内处理请求的速率
合理进行任务拆分,也是利用异步的关键
在异步处理时,经常用到这两个接口
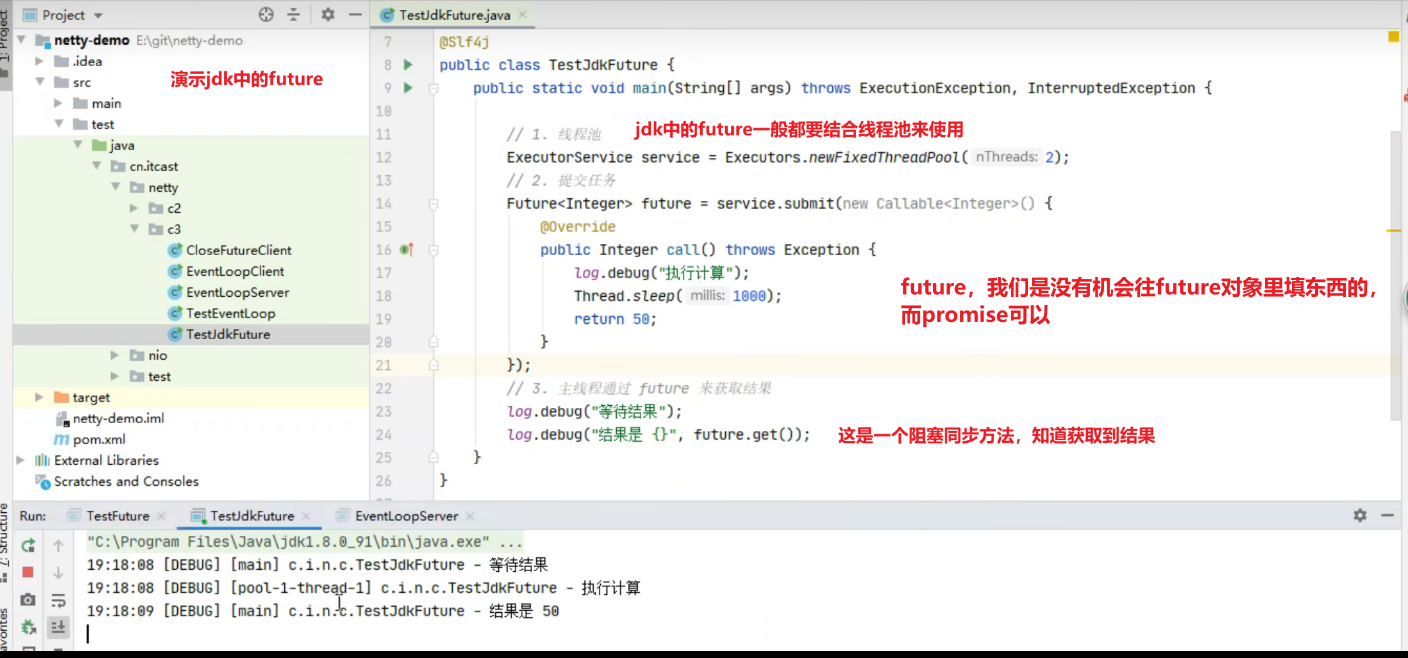
首先要说明 netty 中的 Future 与 jdk 中的 Future 同名,但是是两个接口,netty 的 Future 继承自 jdk 的 Future,而 Promise 又对 netty Future 进行了扩展
jdk Future 只能同步等待任务结束(或成功、或失败)才能得到结果
netty Future 可以同步等待任务结束得到结果,也可以异步方式得到结果,但都是要等任务结束
netty Promise 不仅有 netty Future 的功能,而且脱离了任务独立存在,只作为两个线程间传递结果的容器
功能/名称
jdk Future
netty Future
Promise
cancel
取消任务
-
-
isCanceled
任务是否取消
-
-
isDone
任务是否完成,不能区分成功失败
-
-
get
获取任务结果,阻塞等待
-
-
getNow
-
获取任务结果,非阻塞,还未产生结果时返回 null
-
await
-
等待任务结束,如果任务失败,不会抛异常,而是通过 isSuccess 判断
-
sync
-
等待任务结束,如果任务失败,抛出异常
-
isSuccess
-
判断任务是否成功
-
cause
-
获取失败信息,非阻塞,如果没有失败,返回null
-
addLinstener
-
添加回调,异步接收结果
-
setSuccess
-
-
设置成功结果
setFailure
-
-
设置失败结果
jdk-future
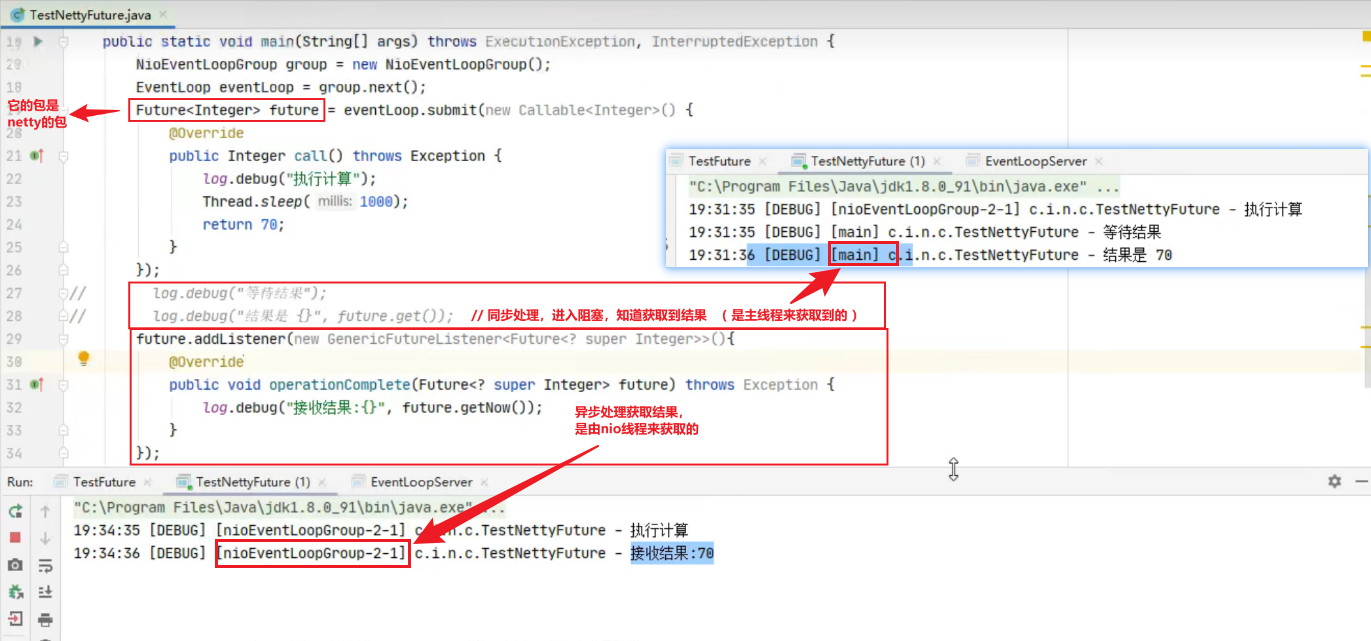
演示netty-future
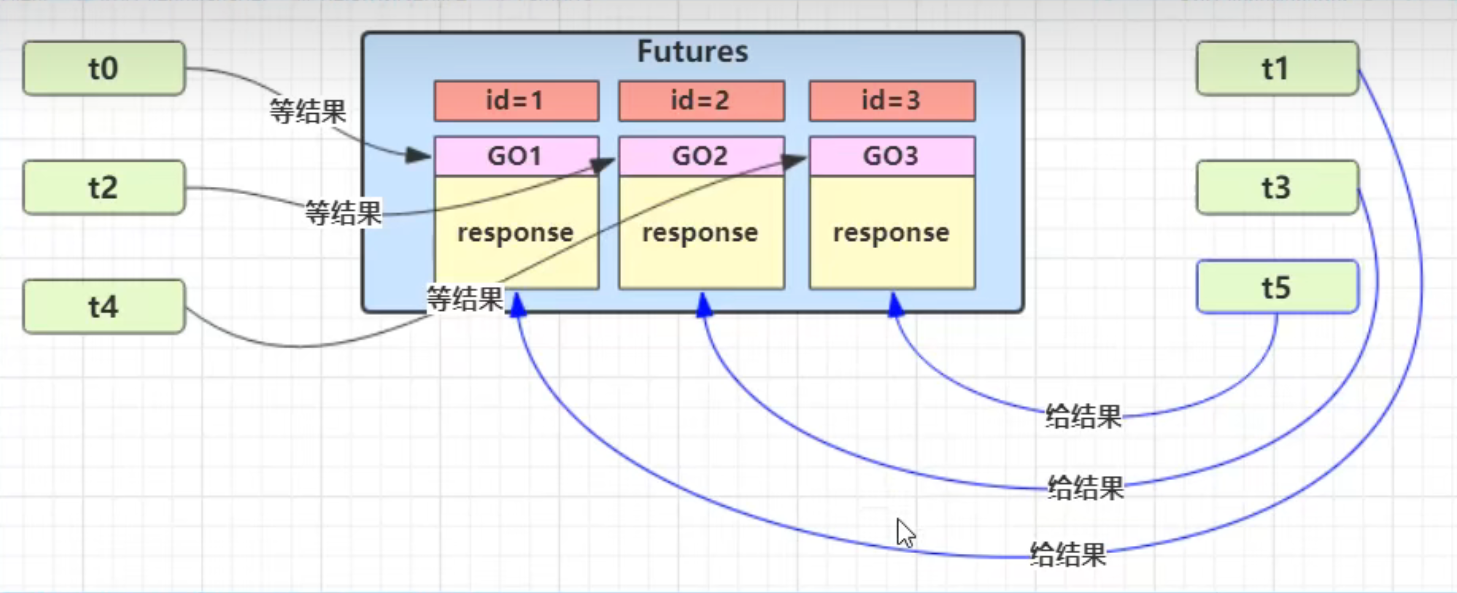
future是被动的,它的创建权和结果设置权都不是我们自己控制,它是由eventLoop.submit提交任务时返回的future。那有没有一个更灵活的方式呢?就是promise对象的使用
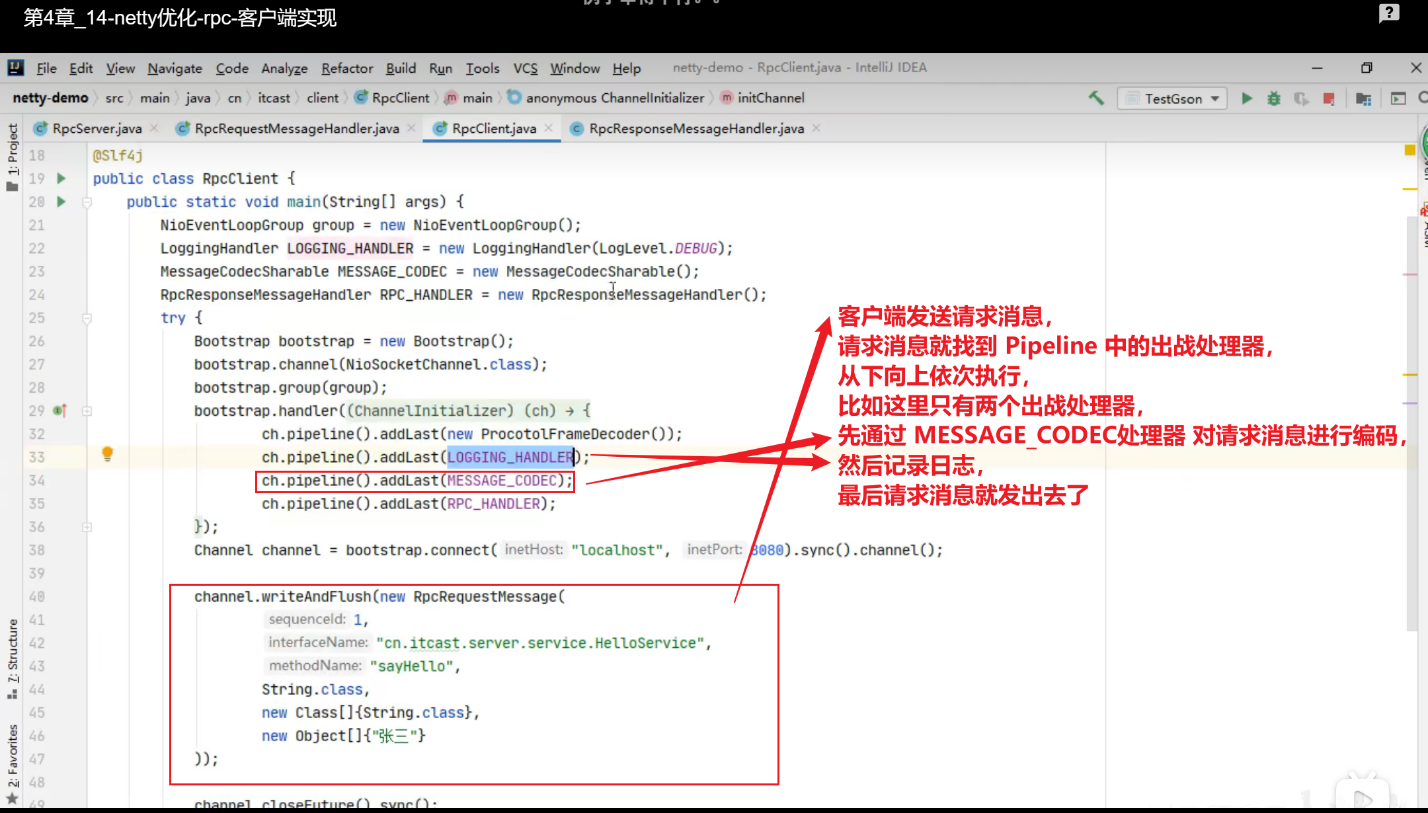
对于网络编程中的 RPC 框架,promise就非常有用,而future肯定不行,必须要用promise
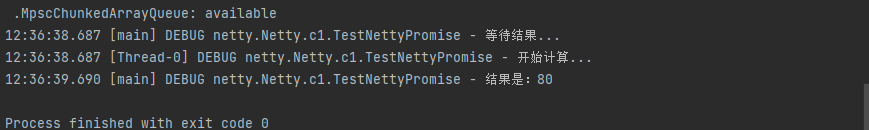
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 import io.netty.channel.EventLoop;import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;import io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultPromise;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;@Slf4j public class TestNettyPromise { public static void main (String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { EventLoop eventLoop = new NioEventLoopGroup ().next(); DefaultPromise<Integer> promise = new DefaultPromise <>(eventLoop); new Thread (() -> { log.debug("开始计算..." ); try { int i = 1 / 0 ; Thread.sleep(1000 ); promise.setSuccess(80 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); promise.setFailure(e); } }).start(); log.debug("等待结果..." ); log.debug("结果是:{}" , promise.get()); } }
int i = 1 / 0 出异常,填充失败结果的运行结果:
int i = 1 / 1 不出异常,填充成功结果的运行结果:
同步处理任务成功
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 DefaultEventLoop eventExecutors = new DefaultEventLoop ();DefaultPromise<Integer> promise = new DefaultPromise <>(eventExecutors); eventExecutors.execute(()->{ try { Thread.sleep(1000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } log.debug("set success, {}" ,10 ); promise.setSuccess(10 ); }); log.debug("start..." ); log.debug("{}" ,promise.getNow()); log.debug("{}" ,promise.get());
输出
1 2 3 4 11:51:53 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - start... 11:51:53 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - null 11:51:54 [DEBUG] [defaultEventLoop-1-1] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - set success, 10 11:51:54 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - 10
异步处理任务成功
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 DefaultEventLoop eventExecutors = new DefaultEventLoop ();DefaultPromise<Integer> promise = new DefaultPromise <>(eventExecutors); promise.addListener(future -> { log.debug("{}" ,future.getNow()); }); eventExecutors.execute(()->{ try { Thread.sleep(1000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } log.debug("set success, {}" ,10 ); promise.setSuccess(10 ); }); log.debug("start..." );
输出
1 2 3 11:49:30 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - start... 11:49:31 [DEBUG] [defaultEventLoop-1-1] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - set success, 10 11:49:31 [DEBUG] [defaultEventLoop-1-1] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - 10
同步处理任务失败 - sync & get
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 DefaultEventLoop eventExecutors = new DefaultEventLoop (); DefaultPromise<Integer> promise = new DefaultPromise <>(eventExecutors); eventExecutors.execute(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(1000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException ("error..." ); log.debug("set failure, {}" , e.toString()); promise.setFailure(e); }); log.debug("start..." ); log.debug("{}" , promise.getNow()); promise.get();
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 12:11:07 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - start... 12:11:07 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - null 12:11:08 [DEBUG] [defaultEventLoop-1-1] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - set failure, java.lang.RuntimeException: error... Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException: java.lang.RuntimeException: error... at io.netty.util.concurrent.AbstractFuture.get(AbstractFuture.java:41) at com.itcast.oio.DefaultPromiseTest2.main(DefaultPromiseTest2.java:34) Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: error... at com.itcast.oio.DefaultPromiseTest2.lambda$main$0(DefaultPromiseTest2.java:27) at io.netty.channel.DefaultEventLoop.run(DefaultEventLoop.java:54) at io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor$5.run(SingleThreadEventExecutor.java:918) at io.netty.util.internal.ThreadExecutorMap$2.run(ThreadExecutorMap.java:74) at io.netty.util.concurrent.FastThreadLocalRunnable.run(FastThreadLocalRunnable.java:30) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745)
同步处理任务失败 - await
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 DefaultEventLoop eventExecutors = new DefaultEventLoop ();DefaultPromise<Integer> promise = new DefaultPromise <>(eventExecutors); eventExecutors.execute(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(1000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException ("error..." ); log.debug("set failure, {}" , e.toString()); promise.setFailure(e); }); log.debug("start..." ); log.debug("{}" , promise.getNow()); promise.await(); log.debug("result {}" , (promise.isSuccess() ? promise.getNow() : promise.cause()).toString());
输出
1 2 3 4 12:18:53 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - start... 12:18:53 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - null 12:18:54 [DEBUG] [defaultEventLoop-1-1] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - set failure, java.lang.RuntimeException: error... 12:18:54 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - result java.lang.RuntimeException: error...
异步处理任务失败
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 DefaultEventLoop eventExecutors = new DefaultEventLoop ();DefaultPromise<Integer> promise = new DefaultPromise <>(eventExecutors); promise.addListener(future -> { log.debug("result {}" , (promise.isSuccess() ? promise.getNow() : promise.cause()).toString()); }); eventExecutors.execute(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(1000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException ("error..." ); log.debug("set failure, {}" , e.toString()); promise.setFailure(e); }); log.debug("start..." );
输出
1 2 3 12:04:57 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - start... 12:04:58 [DEBUG] [defaultEventLoop-1-1] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - set failure, java.lang.RuntimeException: error... 12:04:58 [DEBUG] [defaultEventLoop-1-1] c.i.o.DefaultPromiseTest2 - result java.lang.RuntimeException: error...
await 死锁检查
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 DefaultEventLoop eventExecutors = new DefaultEventLoop ();DefaultPromise<Integer> promise = new DefaultPromise <>(eventExecutors); eventExecutors.submit(()->{ System.out.println("1" ); try { promise.await(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("2" ); }); eventExecutors.submit(()->{ System.out.println("3" ); try { promise.await(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("4" ); });
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 1 2 3 4 io.netty.util.concurrent.BlockingOperationException: DefaultPromise@47499c2a(incomplete) at io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultPromise.checkDeadLock(DefaultPromise.java:384) at io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultPromise.await(DefaultPromise.java:212) at com.itcast.oio.DefaultPromiseTest.lambda$main$0(DefaultPromiseTest.java:27) at io.netty.util.concurrent.PromiseTask$RunnableAdapter.call(PromiseTask.java:38) at io.netty.util.concurrent.PromiseTask.run(PromiseTask.java:73) at io.netty.channel.DefaultEventLoop.run(DefaultEventLoop.java:54) at io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor$5.run(SingleThreadEventExecutor.java:918) at io.netty.util.internal.ThreadExecutorMap$2.run(ThreadExecutorMap.java:74) at io.netty.util.concurrent.FastThreadLocalRunnable.run(FastThreadLocalRunnable.java:30) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745) io.netty.util.concurrent.BlockingOperationException: DefaultPromise@47499c2a(incomplete) at io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultPromise.checkDeadLock(DefaultPromise.java:384) at io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultPromise.await(DefaultPromise.java:212) at com.itcast.oio.DefaultPromiseTest.lambda$main$1(DefaultPromiseTest.java:36) at io.netty.util.concurrent.PromiseTask$RunnableAdapter.call(PromiseTask.java:38) at io.netty.util.concurrent.PromiseTask.run(PromiseTask.java:73) at io.netty.channel.DefaultEventLoop.run(DefaultEventLoop.java:54) at io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor$5.run(SingleThreadEventExecutor.java:918) at io.netty.util.internal.ThreadExecutorMap$2.run(ThreadExecutorMap.java:74) at io.netty.util.concurrent.FastThreadLocalRunnable.run(FastThreadLocalRunnable.java:30) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745)
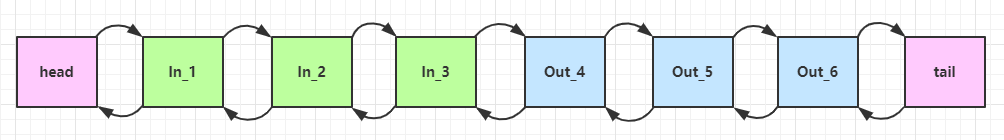
ChannelHandler 用来处理 Channel 上的各种事件,分为入站、出站两种。所有 ChannelHandler 被连成一串,就是 Pipeline
入站处理器通常是 ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter 的子类,主要用来读取客户端数据,写回结果
出站处理器通常是 ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter 的子类,主要对写回结果进行加工
打个比喻,每个 Channel 是一个产品的加工车间,Pipeline 是车间中的流水线,ChannelHandler 就是流水线上的各道工序,而后面要讲的 ByteBuf 是原材料,经过很多工序的加工:先经过一道道入站工序,再经过一道道出站工序最终变成产品
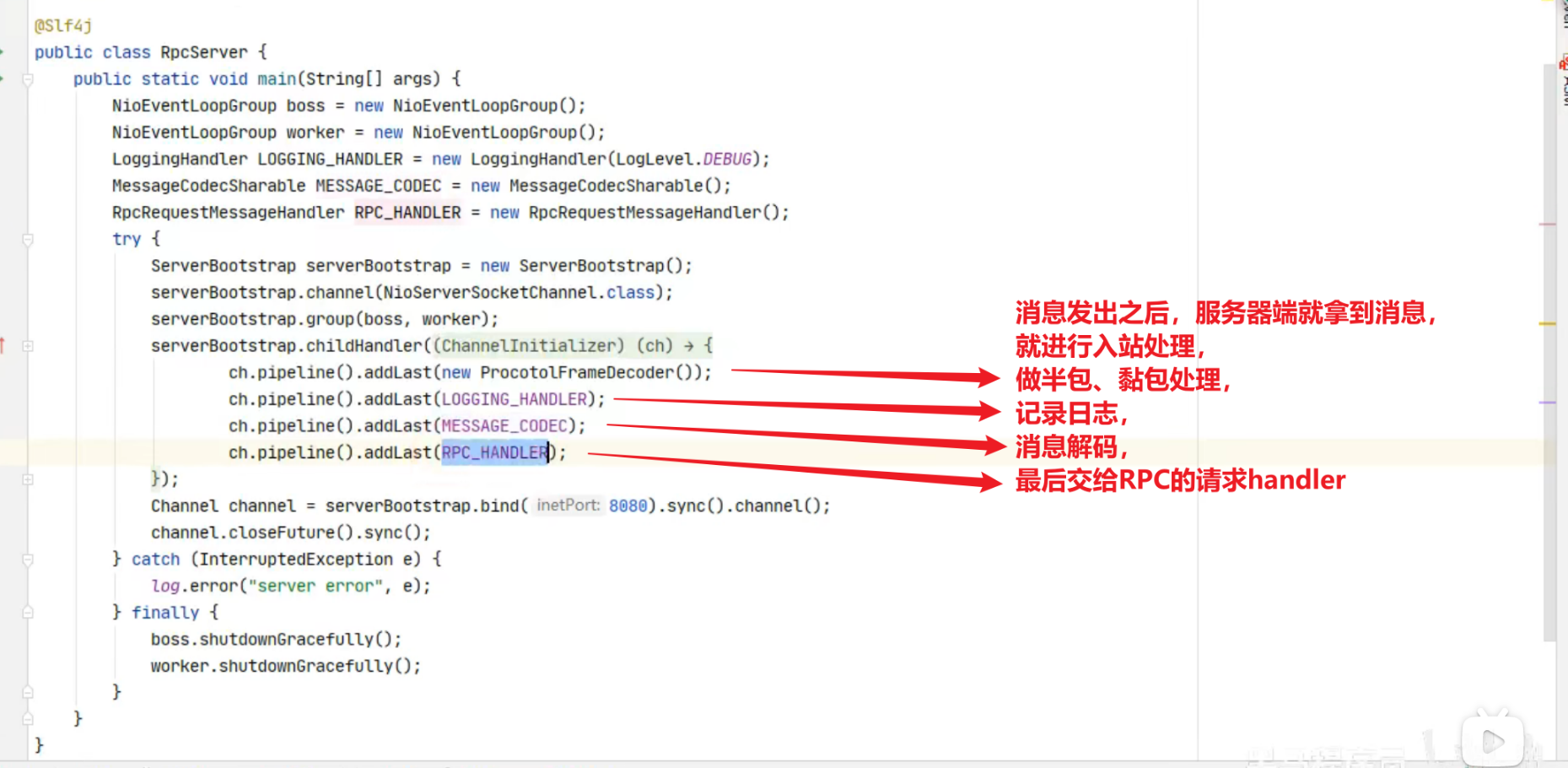
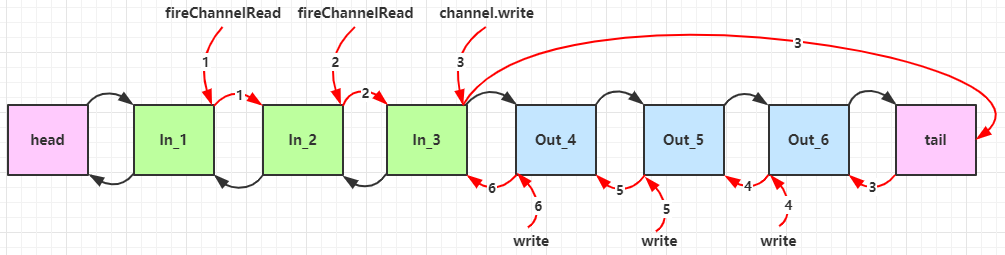
先搞清楚顺序,服务端
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 new ServerBootstrap () .group(new NioEventLoopGroup ()) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer <NioSocketChannel>() { protected void initChannel (NioSocketChannel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter (){ @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { System.out.println(1 ); ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); } }); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter (){ @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { System.out.println(2 ); ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); } }); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter (){ @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { System.out.println(3 ); ctx.channel().write(msg); } }); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter (){ @Override public void write (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) { System.out.println(4 ); ctx.write(msg, promise); } }); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter (){ @Override public void write (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) { System.out.println(5 ); ctx.write(msg, promise); } }); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter (){ @Override public void write (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) { System.out.println(6 ); ctx.write(msg, promise); } }); } }) .bind(8080 );
客户端
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 new Bootstrap () .group(new NioEventLoopGroup ()) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer <Channel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (Channel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder ()); } }) .connect("127.0.0.1" , 8080 ) .addListener((ChannelFutureListener) future -> { future.channel().writeAndFlush("hello,world" ); });
服务器端打印:
可以看到,ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter 是按照 addLast 的顺序执行的,而 ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter 是按照 addLast 的逆序执行的。ChannelPipeline 的实现是一个 ChannelHandlerContext(包装了 ChannelHandler) 组成的双向链表
入站处理器中,ctx.fireChannelRead(msg) 是 调用下一个入站处理器
如果注释掉 1 处代码,则仅会打印 1
如果注释掉 2 处代码,则仅会打印 1 2
3 处的 ctx.channel().write(msg) 会 从尾部开始触发 后续出站处理器的执行
类似的,出站处理器中,ctx.write(msg, promise) 的调用也会 触发上一个出站处理器
如果注释掉 6 处代码,则仅会打印 1 2 3 6
ctx.channel().write(msg) VS ctx.write(msg)
都是触发出站处理器的执行
ctx.channel().write(msg) 从尾部开始查找出站处理器
ctx.write(msg) 是从当前节点找上一个出站处理器
3 处的 ctx.channel().write(msg) 如果改为 ctx.write(msg) 仅会打印 1 2 3,因为节点3 之前没有其它出站处理器了
6 处的 ctx.write(msg, promise) 如果改为 ctx.channel().write(msg) 会打印 1 2 3 6 6 6… 因为 ctx.channel().write() 是从尾部开始查找,结果又是节点6 自己
图1 - 服务端 pipeline 触发的原始流程,图中数字代表了处理步骤的先后次序
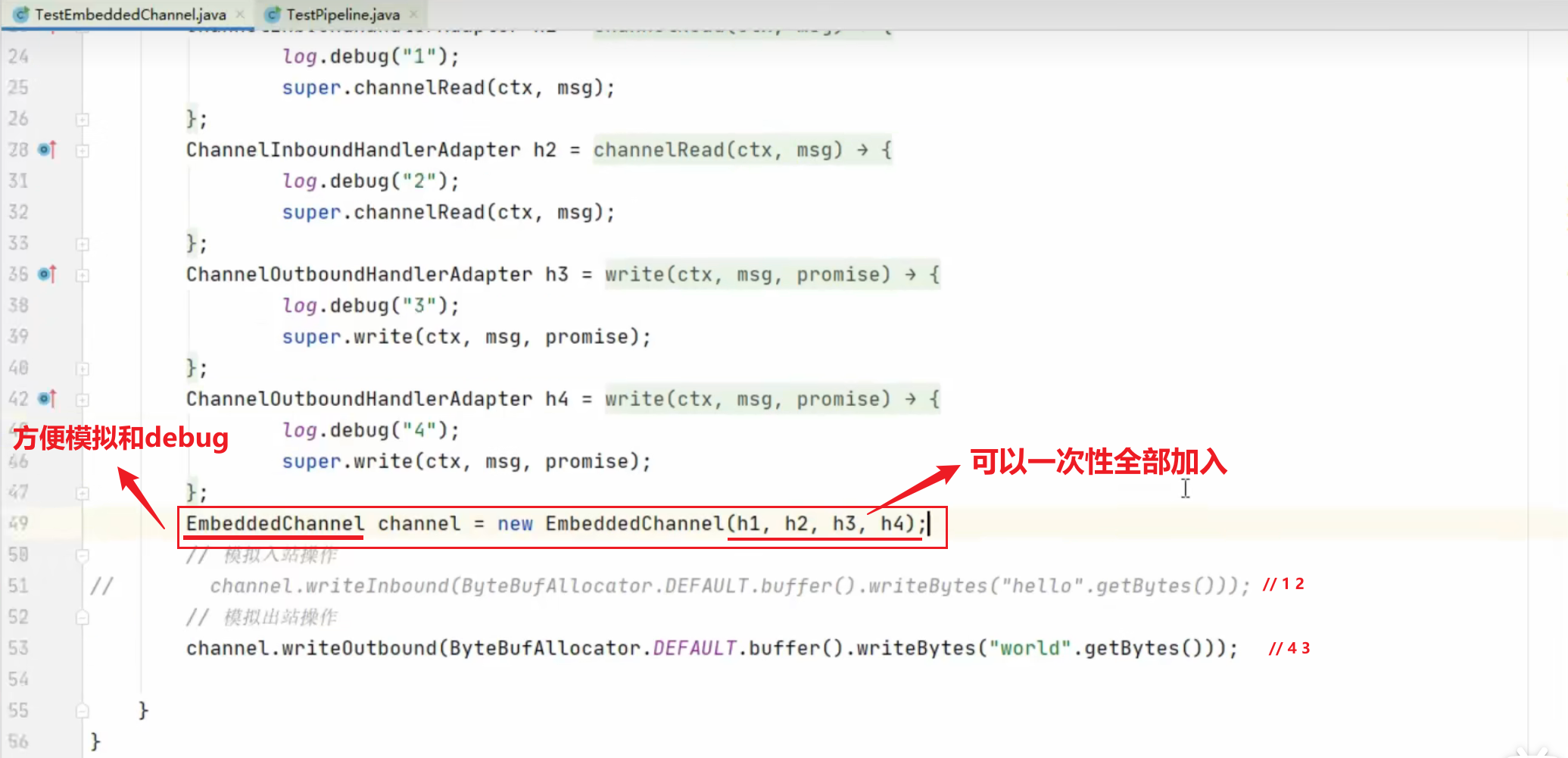
演示EmbeddedChannel ,方便debug和模拟
是对字节数据的封装
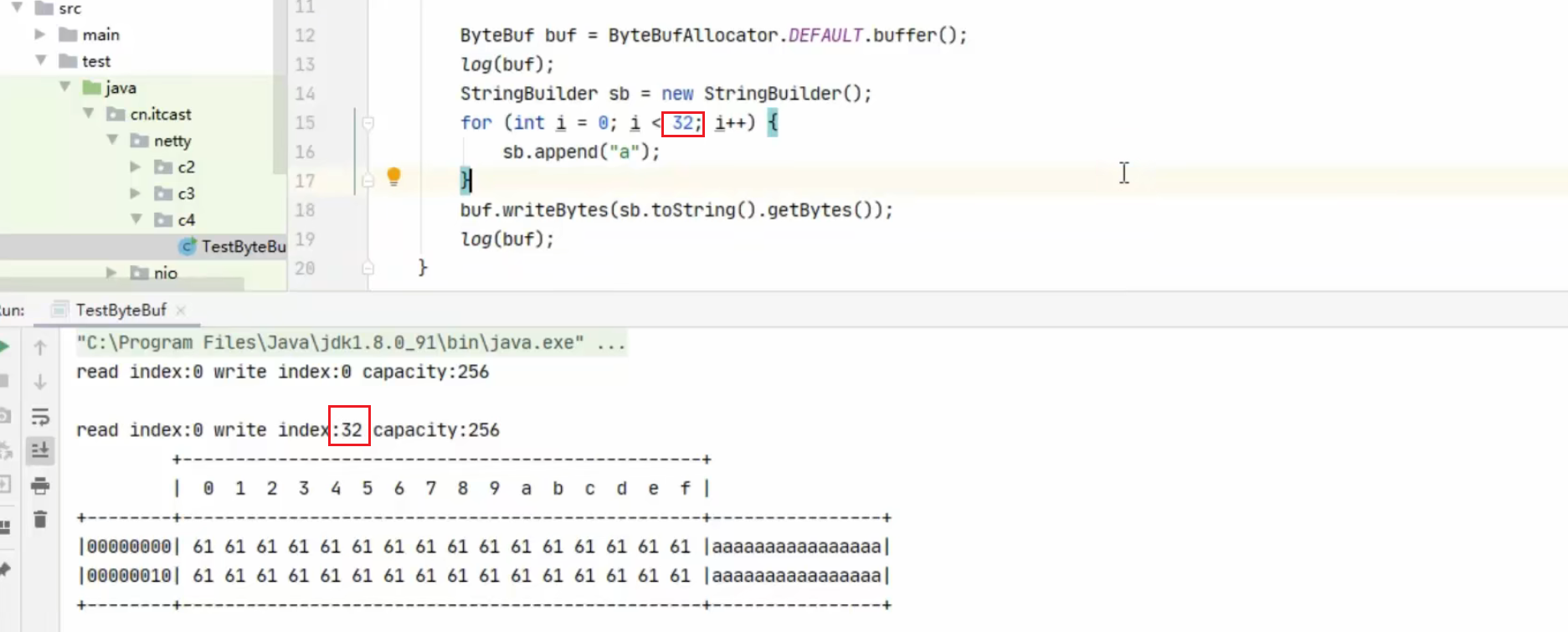
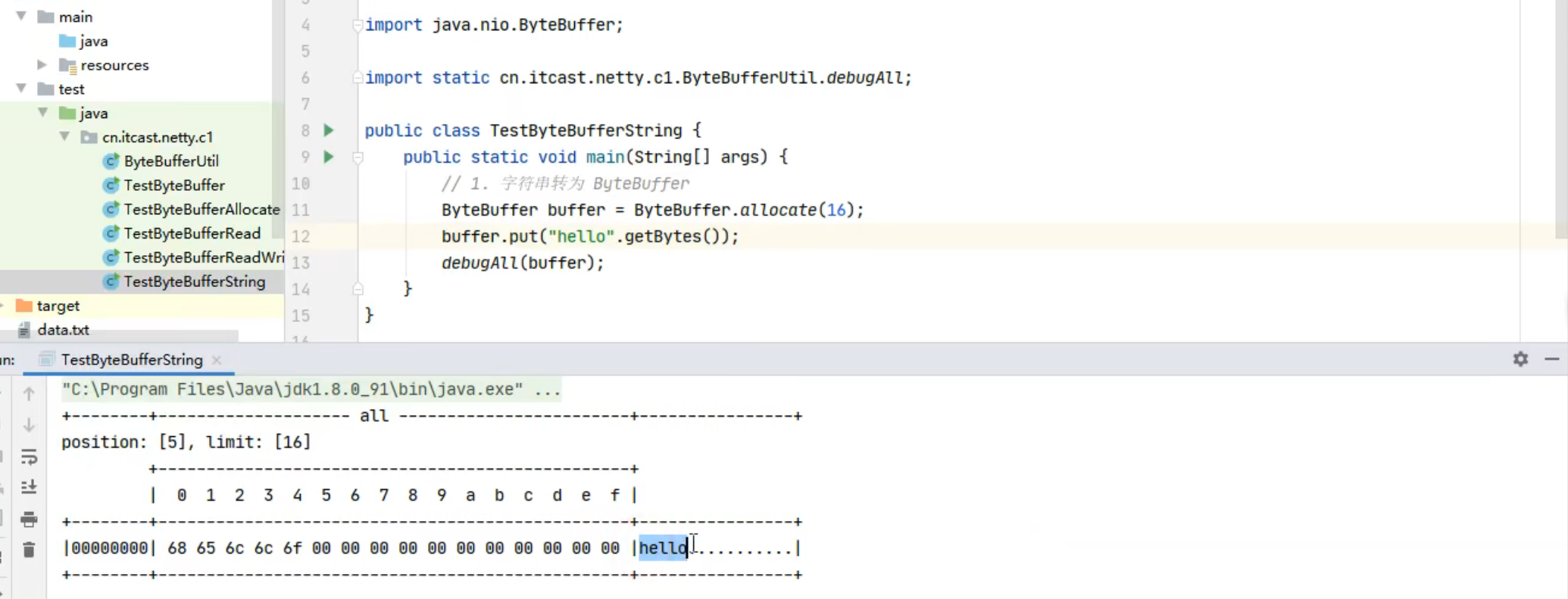
1 2 ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(10 ); log(buffer);
上面代码创建了一个默认的 ByteBuf(池化基于直接内存的 ByteBuf),初始容量是 10
输出
1 read index:0 write index:0 capacity:10
其中 log 方法参考如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 private static void log (ByteBuf buffer) { int length = buffer.readableBytes(); int rows = length / 16 + (length % 15 == 0 ? 0 : 1 ) + 4 ; StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder (rows * 80 * 2 ) .append("read index:" ).append(buffer.readerIndex()) .append(" write index:" ).append(buffer.writerIndex()) .append(" capacity:" ).append(buffer.capacity()) .append(NEWLINE); appendPrettyHexDump(buf, buffer); System.out.println(buf.toString()); }
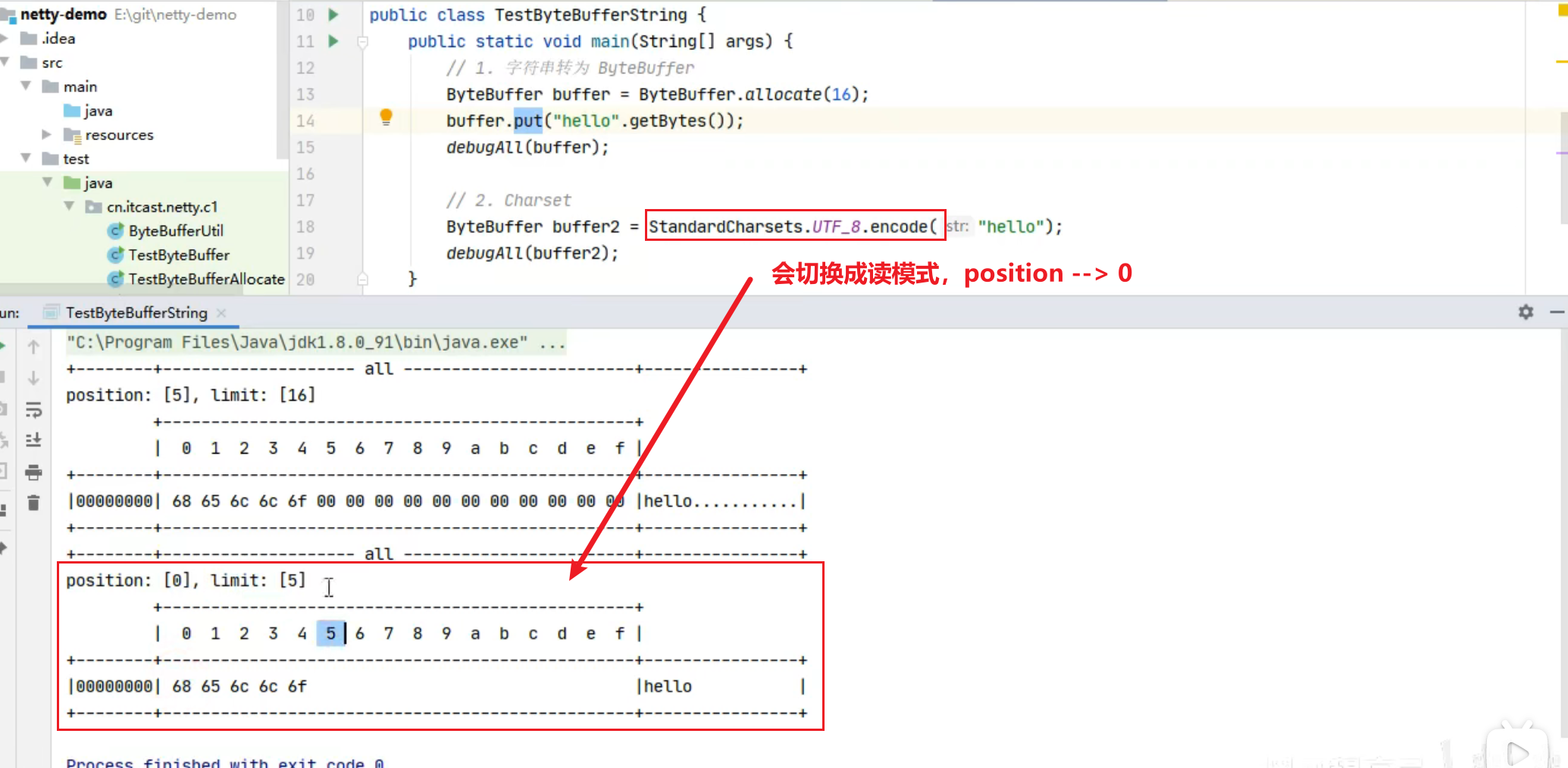
演示动态扩容
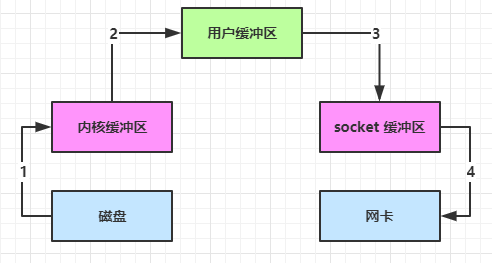
直接内存 分配效率低读,写效率高(直接内存使用的是系统内存,如果你比如说磁盘中读取文件时,它可以将这个数据直接入系统内存,那么这个系统内存呢,就可以用直接内存方式映射到Java内存,映射到Java中,Java里面访问的跟操作系统访问的是同一块内存,这样就可以减少一次内存复制。所以直接内存的读写效率是高于堆内存发的);
堆内存 分配效率高,读写效率高(因为堆内存要受到GC的影响,GC必然会发生一些对象的很搬迁、复制)
所以netty默认使用的是直接内存来作为ByteBuf的内存(但也可以通过使用不同的方法来选择 直接内存 or 堆内存)
可以使用下面的代码来创建池化基于堆的 ByteBuf
1 ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.heapBuffer(10 );
也可以使用下面的代码来创建池化基于直接内存的 ByteBuf
1 ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.directBuffer(10 );
直接内存创建和销毁的代价昂贵,但读写性能高(少一次内存复制),适合配合池化功能一起用
直接内存对 GC 压力小,因为这部分内存不受 JVM 垃圾回收的管理,但也要注意及时主动释放
池化的最大意义在于可以重用 ByteBuf ,优点有
没有池化,则每次都得创建新的 ByteBuf 实例,这个操作对直接内存代价昂贵,就算是堆内存,也会增加 GC 压力
有了池化,则可以重用池中 ByteBuf 实例,并且采用了与 jemalloc 类似的内存分配算法提升分配效率
高并发时,池化功能更节约内存,减少内存溢出的可能
池化功能是否开启,可以通过下面的系统环境变量来设置
1 -Dio.netty.allocator.type={unpooled|pooled}
4.1 以后,非 Android 平台默认启用池化实现,Android 平台启用非池化实现
4.1 之前,池化功能还不成熟,默认是非池化实现
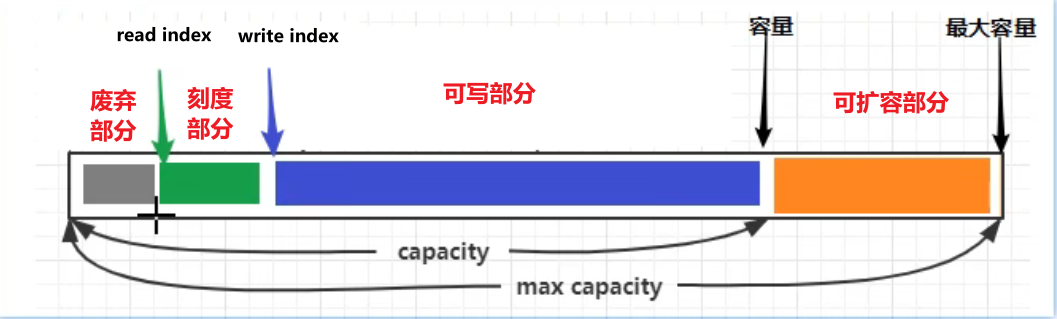
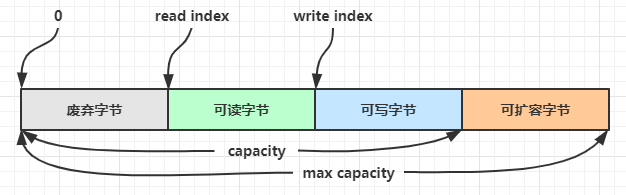
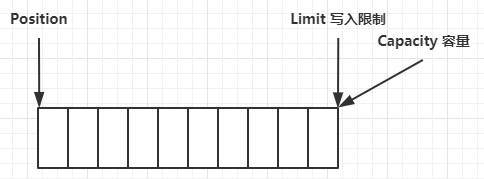
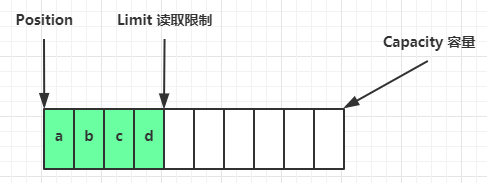
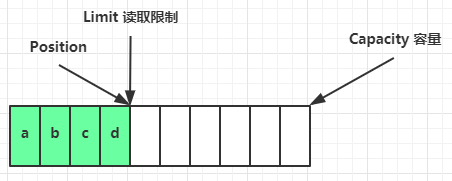
ByteBuf 由四部分组成
最开始读写指针都在 0 位置
优势:ByteBuf从两方面进行了改进:
有读、写两个指针,就不用来回切换读写模式了,只要有可写、可读的都可以执行。而ByteBuffer是要读就切换到读模式,要写切换到写模式,
可以动态扩容。不会因为开始容量计算失误计算少了而导致因为内存不够报异常,ByteBuf只要在最大容量内( <= 整数的最大值),可扩容部分会根据实际写入的字节进行扩容
方法列表,省略一些不重要的方法
方法签名
含义
备注
writeBoolean(boolean value)
写入 boolean 值
用一字节 01|00 代表 true|false
writeByte(int value)
写入 byte 值
writeShort(int value)
写入 short 值
writeInt(int value)
写入 int 值
Big Endian(大端),即 0x250,写入后 00 00 02 50
writeIntLE(int value)
写入 int 值
Little Endian(小端),即 0x250,写入后 50 02 00 00
writeLong(long value)
写入 long 值
writeChar(int value)
写入 char 值
writeFloat(float value)
写入 float 值
writeDouble(double value)
写入 double 值
writeBytes(ByteBuf src)
写入 netty 的 ByteBuf
writeBytes(byte[] src)
写入 byte[]
writeBytes(ByteBuffer src)
写入 nio 的 ByteBuffer
int writeCharSequence(CharSequence sequence, Charset charset)
写入字符串
注意
这些方法的未指明返回值的,其返回值都是 ByteBuf,意味着可以链式调用
网络传输,默认习惯是 Big Endian
先写入 4 个字节
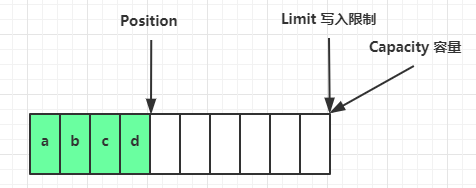
1 2 buffer.writeBytes(new byte []{1 , 2 , 3 , 4 }); log(buffer);
结果是
1 2 3 4 5 6 read index:0 write index:4 capacity:10 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 01 02 03 04 |.... | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
再写入一个 int 整数,也是 4 个字节
1 2 buffer.writeInt(5 ); log(buffer);
结果是
1 2 3 4 5 6 read index:0 write index:8 capacity:10 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 01 02 03 04 00 00 00 05 |........ | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
还有一类方法是 set 开头的一系列方法,也可以写入数据,但不会改变写指针位置
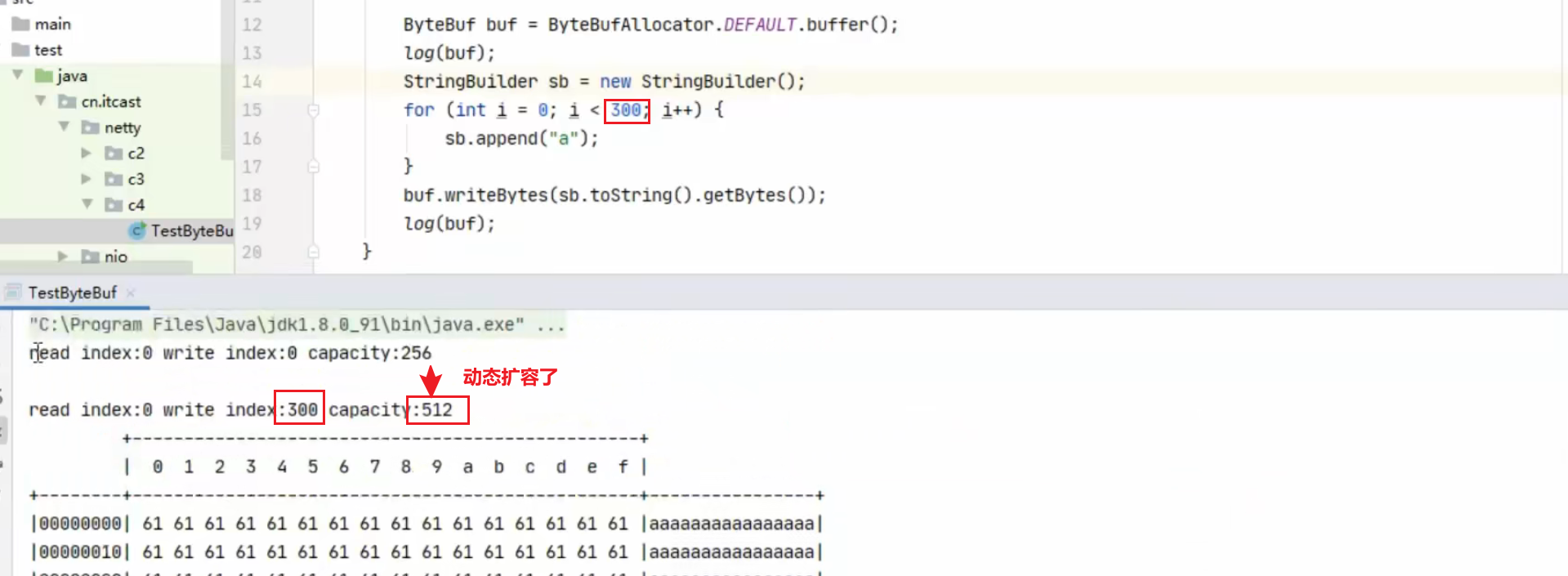
再写入一个 int 整数时,容量不够了(初始容量是 10),这时会引发扩容
1 2 buffer.writeInt(6 ); log(buffer);
扩容规则是
如何写入后数据大小未超过 512,则选择下一个 16 的整数倍,例如写入后大小为 12 ,则扩容后 capacity 是 16
如果写入后数据大小超过 512,则选择下一个 2^n,例如写入后大小为 513,则扩容后 capacity 是 210=1024(2 9=512 已经不够了)
扩容不能超过 max capacity 会报错
结果是
1 2 3 4 5 6 read index:0 write index:12 capacity:16 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 01 02 03 04 00 00 00 05 00 00 00 06 |............ | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
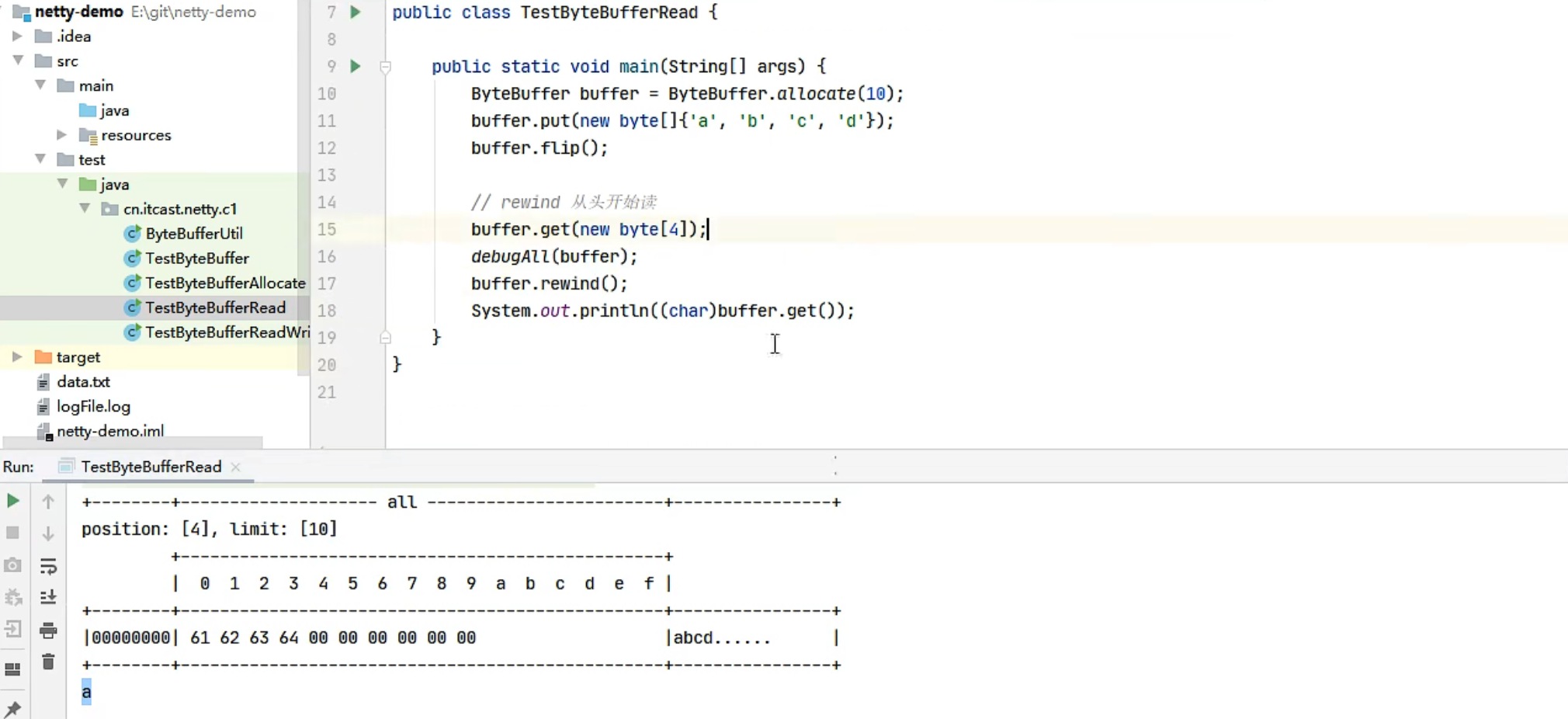
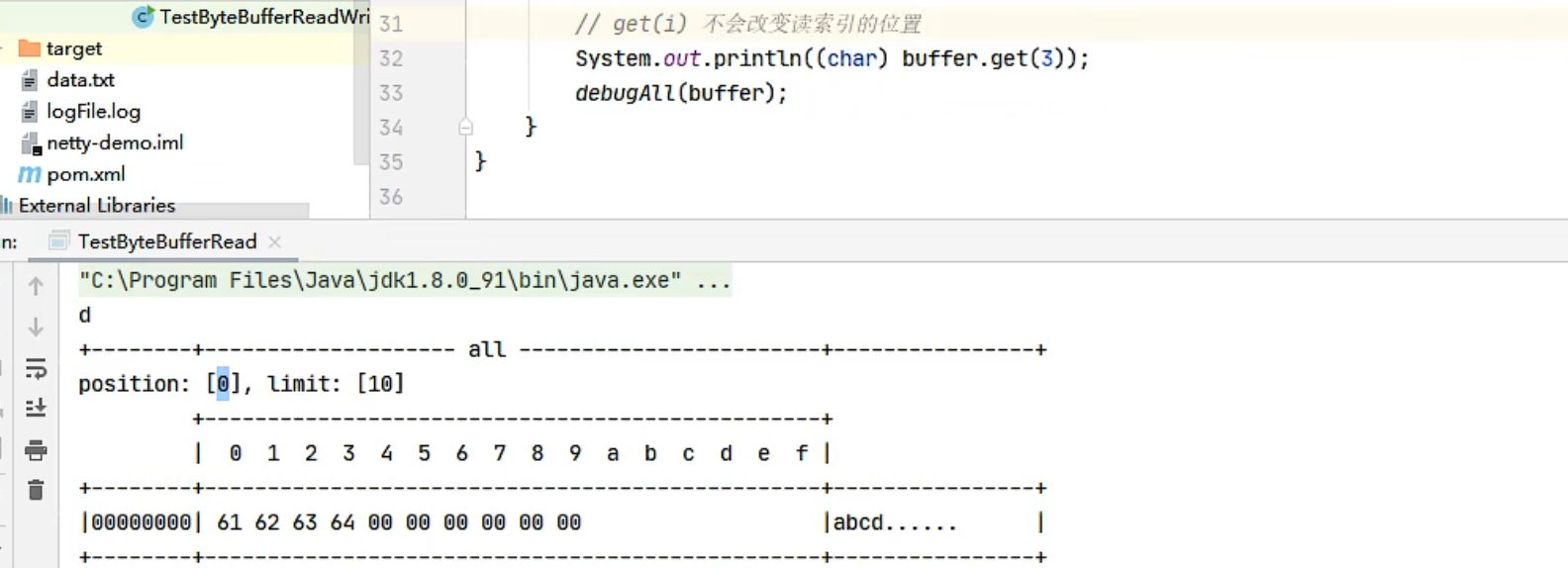
例如读了 4 次,每次一个字节
1 2 3 4 5 System.out.println(buffer.readByte()); System.out.println(buffer.readByte()); System.out.println(buffer.readByte()); System.out.println(buffer.readByte()); log(buffer);
读过的内容,就属于废弃部分了,再读只能读那些尚未读取的部分
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 read index:4 write index:12 capacity:16 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 00 00 00 05 00 00 00 06 |........ | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
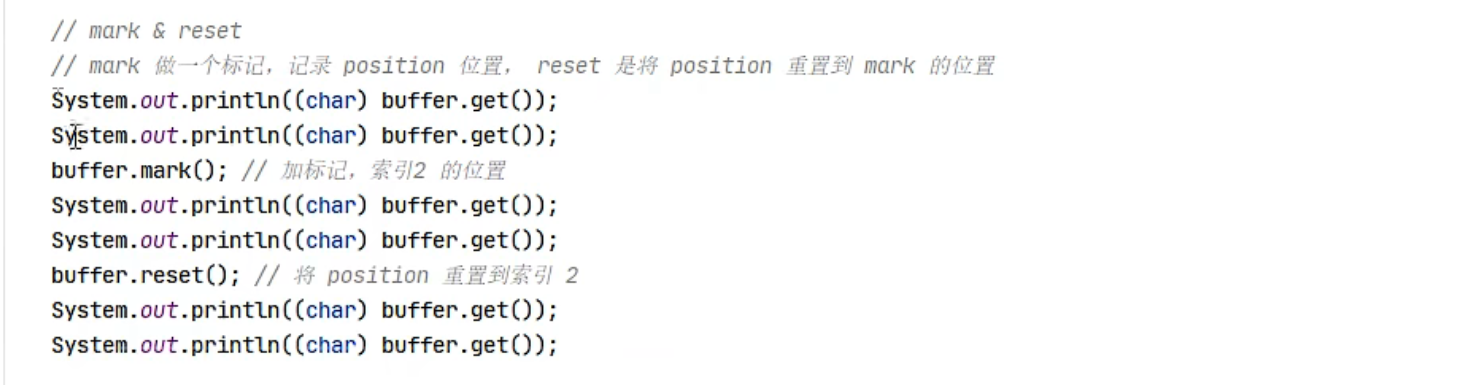
如果需要重复读取 int 整数 5,怎么办?
可以在 read 前先做个标记 mark
1 2 3 buffer.markReaderIndex(); System.out.println(buffer.readInt()); log(buffer);
结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 5 read index:8 write index:12 capacity:16 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 00 00 00 06 |.... | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
这时要重复读取的话,重置到标记位置 reset
1 2 buffer.resetReaderIndex(); log(buffer);
这时
1 2 3 4 5 6 read index:4 write index:12 capacity:16 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 00 00 00 05 00 00 00 06 |........ | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
还有种办法是采用 get 开头的一系列方法,这些方法不会改变 read index
由于 Netty 中有堆外内存的 ByteBuf 实现,堆外内存最好是手动来释放,而不是等 GC 垃圾回收。
UnpooledHeapByteBuf 使用的是 JVM 内存,只需等 GC 回收内存即可
UnpooledDirectByteBuf 使用的就是直接内存了,需要特殊的方法来回收内存
PooledByteBuf 和它的子类使用了池化机制,需要更复杂的规则来回收内存
回收内存的源码实现,请关注下面方法的不同实现
protected abstract void deallocate()
Netty 这里采用了引用计数法来控制回收内存,每个 ByteBuf 都实现了 ReferenceCounted 接口
每个 ByteBuf 对象的初始计数为 1
调用 release 方法计数减 1,如果计数为 0,ByteBuf 内存被回收
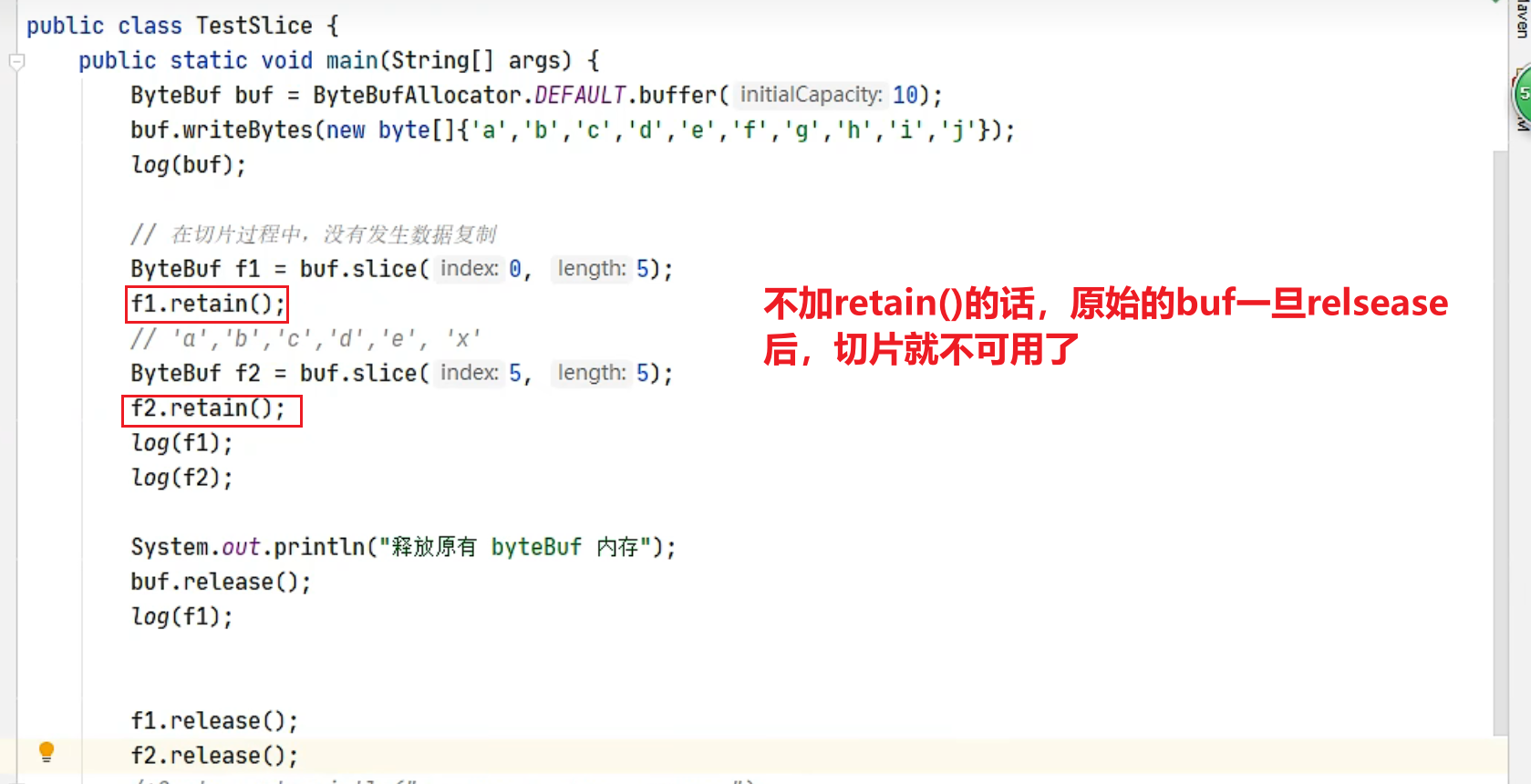
调用 retain 方法计数加 1,表示调用者没用完之前,其它 handler 即使调用了 release 也不会造成回收
当计数为 0 时,底层内存会被回收,这时即使 ByteBuf 对象还在,其各个方法均无法正常使用
谁来负责 release 呢?
不是我们想象的(一般情况下)
1 2 3 4 5 6 ByteBuf buf = ...try { ... } finally { buf.release(); }
请思考,因为 pipeline 的存在,一般需要将 ByteBuf 传递给下一个 ChannelHandler,如果在 finally 中 release 了,就失去了传递性(当然,如果在这个 ChannelHandler 内这个 ByteBuf 已完成了它的使命,那么便无须再传递)
基本规则是,谁是最后使用者,谁负责 release ,详细分析如下
起点,对于 NIO 实现来讲,在 io.netty.channel.nio.AbstractNioByteChannel.NioByteUnsafe#read 方法中首次创建 ByteBuf 放入 pipeline(line 163 pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf))
入站 ByteBuf 处理原则
对原始 ByteBuf 不做处理,调用 ctx.fireChannelRead(msg) 向后传递,这时无须 release
将原始 ByteBuf 转换为其它类型的 Java 对象,这时 ByteBuf 就没用了,必须 release
如果不调用 ctx.fireChannelRead(msg) 向后传递,那么也必须 release
注意各种异常,如果 ByteBuf 没有成功传递到下一个 ChannelHandler,必须 release
假设消息一直向后传,那么 TailContext 会负责释放未处理消息(原始的 ByteBuf)
出站 ByteBuf 处理原则
出站消息最终都会转为 ByteBuf 输出,一直向前传,由 HeadContext flush 后 release
异常处理原则
有时候不清楚 ByteBuf 被引用了多少次,但又必须彻底释放,可以循环调用 release 直到返回 true
TailContext 释放未处理消息逻辑
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 protected void onUnhandledInboundMessage (Object msg) { try { logger.debug( "Discarded inbound message {} that reached at the tail of the pipeline. " + "Please check your pipeline configuration." , msg); } finally { ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg); } }
具体代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public static boolean release (Object msg) { if (msg instanceof ReferenceCounted) { return ((ReferenceCounted) msg).release(); } return false ; }
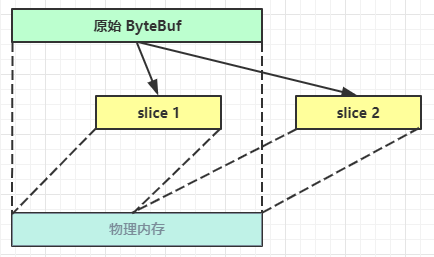
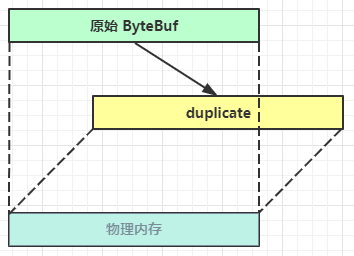
【零拷贝】的体现之一,对原始 ByteBuf 进行切片成多个 ByteBuf,切片后的 ByteBuf 并没有发生内存复制,还是使用原始 ByteBuf 的内存,切片后的 ByteBuf 维护独立的 read,write 指针
例,原始 ByteBuf 进行一些初始操作
1 2 3 4 ByteBuf origin = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(10 );origin.writeBytes(new byte []{1 , 2 , 3 , 4 }); origin.readByte(); System.out.println(ByteBufUtil.prettyHexDump(origin));
输出
1 2 3 4 5 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 02 03 04 |... | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
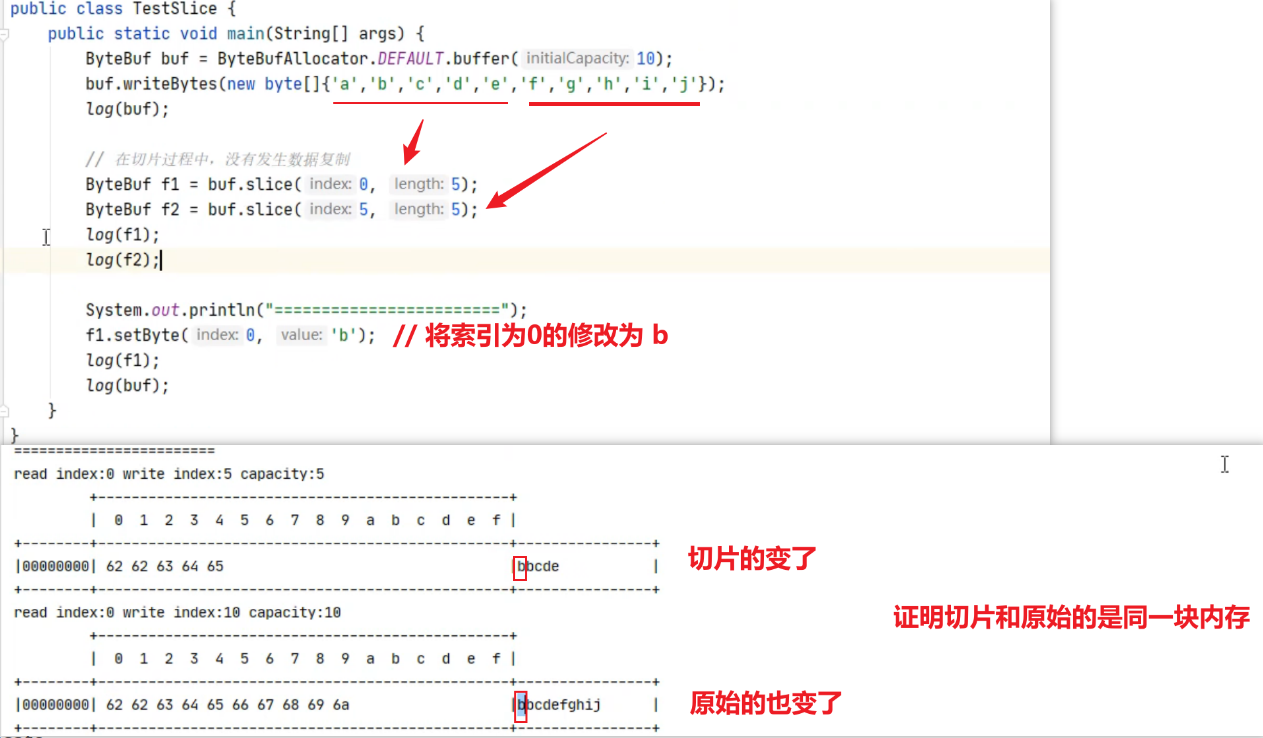
这时调用 slice 进行切片,无参 slice 是从原始 ByteBuf 的 read index 到 write index 之间的内容进行切片,切片后的 max capacity 被固定为这个区间的大小,因此不能追加 write
1 2 3 ByteBuf slice = origin.slice();System.out.println(ByteBufUtil.prettyHexDump(slice));
输出
1 2 3 4 5 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 02 03 04 |... | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
如果原始 ByteBuf 再次读操作(又读了一个字节)
1 2 origin.readByte(); System.out.println(ByteBufUtil.prettyHexDump(origin));
输出
1 2 3 4 5 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 03 04 |.. | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
这时的 slice 不受影响,因为它有独立的读写指针
1 System.out.println(ByteBufUtil.prettyHexDump(slice));
输出
1 2 3 4 5 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 02 03 04 |... | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
如果 slice 的内容发生了更改
1 2 slice.setByte(2 , 5 ); System.out.println(ByteBufUtil.prettyHexDump(slice));
输出
1 2 3 4 5 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 02 03 05 |... | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
这时,原始 ByteBuf 也会受影响,因为底层都是同一块内存
1 System.out.println(ByteBufUtil.prettyHexDump(origin));
输出
1 2 3 4 5 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 03 05 |.. | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
retain()
【零拷贝】的体现之一,就好比截取了原始 ByteBuf 所有内容,并且没有 max capacity 的限制,也是与原始 ByteBuf 使用同一块底层内存,只是读写指针是独立的
会将底层内存数据进行深拷贝,因此无论读写,都与原始 ByteBuf 无关
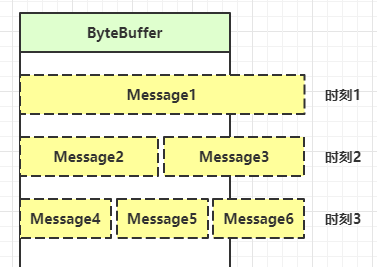
【零拷贝】的体现之一,可以将多个 ByteBuf 合并为一个逻辑上的 ByteBuf,避免拷贝
有两个 ByteBuf 如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 ByteBuf buf1 = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(5 );buf1.writeBytes(new byte []{1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 }); ByteBuf buf2 = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(5 );buf2.writeBytes(new byte []{6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 }); System.out.println(ByteBufUtil.prettyHexDump(buf1)); System.out.println(ByteBufUtil.prettyHexDump(buf2));
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 01 02 03 04 05 |..... | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 06 07 08 09 0a |..... | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
现在需要一个新的 ByteBuf,内容来自于刚才的 buf1 和 buf2,如何实现?
方法1:
1 2 3 4 5 ByteBuf buf3 = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT .buffer(buf1.readableBytes()+buf2.readableBytes()); buf3.writeBytes(buf1); buf3.writeBytes(buf2); System.out.println(ByteBufUtil.prettyHexDump(buf3));
结果
1 2 3 4 5 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a |.......... | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
这种方法好不好?回答是不太好,因为进行了数据的内存复制操作
方法2:
1 2 3 CompositeByteBuf buf3 = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.compositeBuffer();buf3.addComponents(true , buf1, buf2);
结果是一样的
1 2 3 4 5 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a |.......... | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
CompositeByteBuf 是一个组合的 ByteBuf,它内部维护了一个 Component 数组,每个 Component 管理一个 ByteBuf,记录了这个 ByteBuf 相对于整体偏移量等信息,代表着整体中某一段的数据。
优点,对外是一个虚拟视图,组合这些 ByteBuf 不会产生内存复制
缺点,复杂了很多,多次操作会带来性能的损耗
Unpooled 是一个工具类,类如其名,提供了非池化的 ByteBuf 创建、组合、复制等操作
这里仅介绍其跟【零拷贝】相关的 wrappedBuffer 方法,可以用来包装 ByteBuf
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ByteBuf buf1 = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(5 );buf1.writeBytes(new byte []{1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 }); ByteBuf buf2 = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(5 );buf2.writeBytes(new byte []{6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 }); ByteBuf buf3 = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(buf1, buf2);System.out.println(ByteBufUtil.prettyHexDump(buf3));
输出
1 2 3 4 5 +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a |.......... | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
也可以用来包装普通字节数组,底层也不会有拷贝操作
1 2 3 ByteBuf buf4 = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(new byte []{1 , 2 , 3 }, new byte []{4 , 5 , 6 });System.out.println(buf4.getClass()); System.out.println(ByteBufUtil.prettyHexDump(buf4));
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 class io.netty.buffer.CompositeByteBuf +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 01 02 03 04 05 06 |...... | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
池化 - 可以重用池中 ByteBuf 实例,更节约内存,减少内存溢出的可能
读写指针分离,不需要像 ByteBuffer 一样切换读写模式
可以自动扩容
支持链式调用,使用更流畅
很多地方体现零拷贝,例如 slice、duplicate、CompositeByteBuf
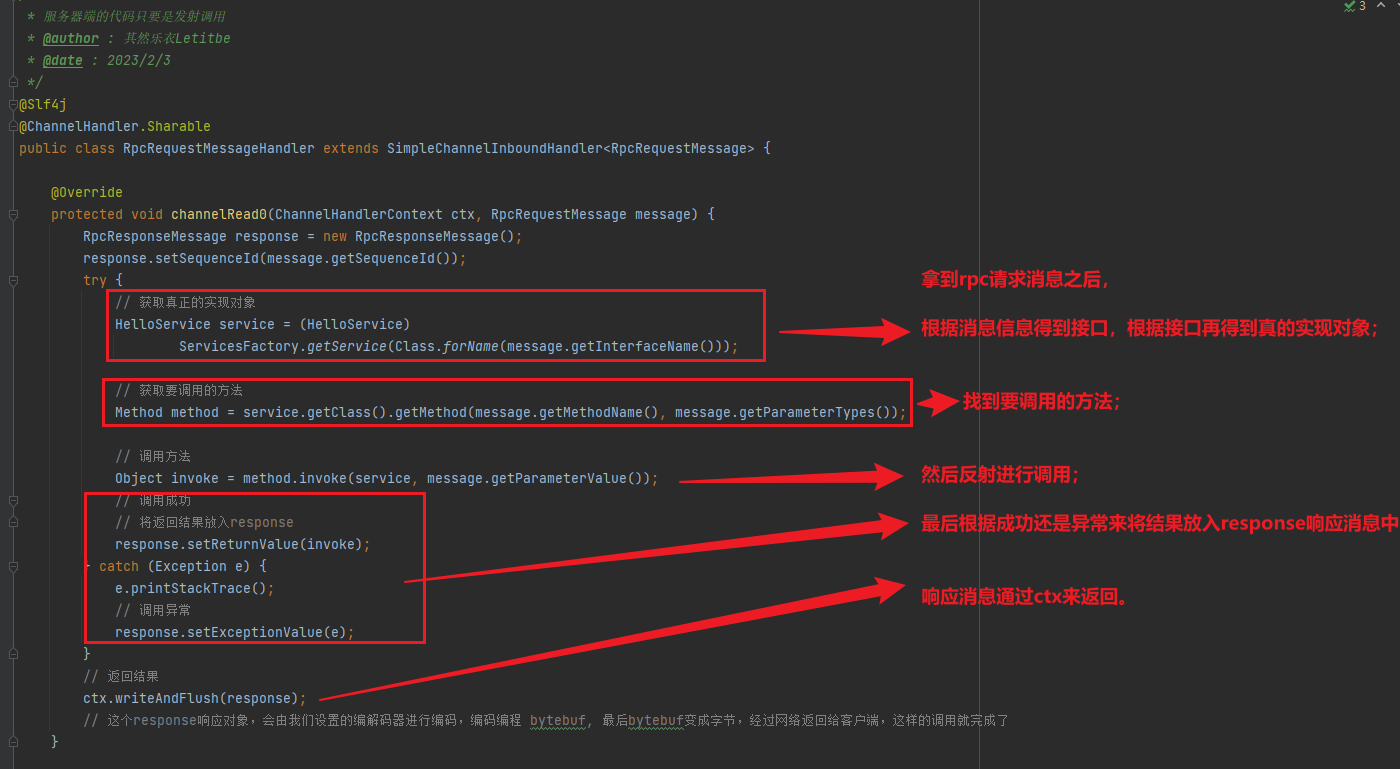
实现一个 echo server
编写 server
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 new ServerBootstrap () .group(new NioEventLoopGroup ()) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer <NioSocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (NioSocketChannel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter (){ @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { ByteBuf buffer = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println(buffer.toString(Charset.defaultCharset())); ByteBuf response = ctx.alloc().buffer(); response.writeBytes(buffer); ctx.writeAndFlush(response); } }); } }).bind(8080 );
编写 client
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup ();Channel channel = new Bootstrap () .group(group) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer <NioSocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder ()); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter () { @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { ByteBuf buffer = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println(buffer.toString(Charset.defaultCharset())); } }); } }).connect("127.0.0.1" , 8080 ).sync().channel(); channel.closeFuture().addListener(future -> { group.shutdownGracefully(); }); new Thread (() -> { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); while (true ) { String line = scanner.nextLine(); if ("q" .equals(line)) { channel.close(); break ; } channel.writeAndFlush(line); } }).start();
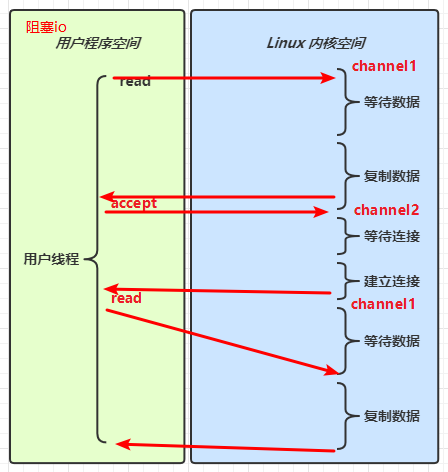
我最初在认识上有这样的误区,认为只有在 netty,nio 这样的多路复用 IO 模型时,读写才不会相互阻塞,才可以实现高效的双向通信,但实际上,Java Socket 是全双工的:在任意时刻,线路上存在A 到 B 和 B 到 A 的双向信号传输。即使是阻塞 IO,读和写是可以同时进行的,只要分别采用读线程和写线程即可,读不会阻塞写、写也不会阻塞读
例如
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public class TestServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket (8888 ); Socket s = ss.accept(); new Thread (() -> { try { BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (s.getInputStream())); while (true ) { System.out.println(reader.readLine()); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); new Thread (() -> { try { BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter (new OutputStreamWriter (s.getOutputStream())); for (int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i++) { writer.write(String.valueOf(i)); writer.newLine(); writer.flush(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); } }
客户端
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class TestClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { Socket s = new Socket ("localhost" , 8888 ); new Thread (() -> { try { BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (s.getInputStream())); while (true ) { System.out.println(reader.readLine()); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); new Thread (() -> { try { BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter (new OutputStreamWriter (s.getOutputStream())); for (int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i++) { writer.write(String.valueOf(i)); writer.newLine(); writer.flush(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); } }